
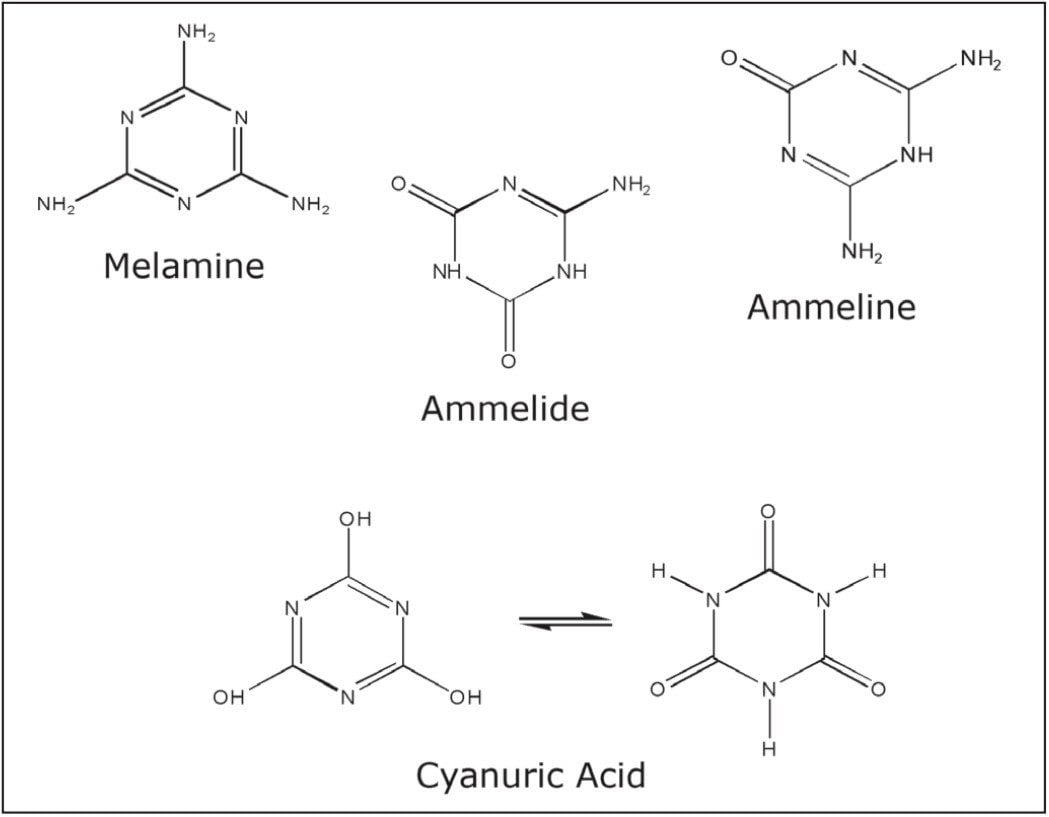
This document presents two methods, the first a Waters ACQUITY UltraPerformance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC) photodiode array (PDA) method that can be used for high concentrations of the materials of interest and the second an ACQUITY UPLC-MS/MS application that can be used for ppb levels of concentration. One of the materials of interest, ammelide, was commercially unavailable at the time of writing and thus was not included in these methods. This compound is not thought to be related to the toxicity issue and therefore not critical to the analysis. Both methods provide results in less than two minutes.
The recent pet food contamination incident in North America highlights the need for conclusive, rapid analyses for melamine and its metabolites (ammeline, ammelide, and cyanuric acid) in pet food, animal feed, and tissue samples. As documented in the Washington Post on May 7, 2007, an unknown number of cats and dogs in the U.S. became ill or died from eating certain brands of pet food. This resulted in the recall of millions of pounds pet food. The formation of sharp melamine-cyanuric acid crystals in the kidneys of animals that consumed the tainted pet food was found to be the probable cause of illness, in some cases leading to death. This outbreak has fueled the latest public outcry for more accurate and rapid analytical food safety testing among manufacturers and government regulatory agencies.
Confirming the widespread nature of this contamination, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) reported that melamine was found in wheat gluten and rice protein concentrate in the U.S., all imported from China and intended for use in pet food.1 Melamine contamination has also been found in animal feed2 causing concern about migration of these products into the human food supply.
This document presents two methods, the first a Waters ACQUITY UltraPerformance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC) photodiode array (PDA) method that can be used for high concentrations of the materials of interest and the second an ACQUITY UPLC-MS/MS application that can be used for ppb levels of concentration. One of the materials of interest, ammelide, was commercially unavailable at the time of writing and thus was not included in these methods. This compound is not thought to be related to the toxicity issue and therefore not critical to the analysis. Both methods provide results in less than two minutes.

Weigh 0.10–1 g of pet food
Extract in 5–10 mL 2% ammonium hydroxide
Filter through a 0.45 micron syringe filter
Mix 100 μL filtrate with 900 μL mobile phase and inject
Melamine, ammeline, and cyanuric acid were obtained from TCI America. Dry dog food was purchased from a local supermarket. The cyanuric acid stock standard was prepared by dissolving in water. The melamine and ammeline stock standards were prepared by dissolving in water/0.1% sodium hydroxide. The stock standards were further diluted with 10 mM ammonium acetate in 90/10 acetonitrile/water to desired concentration level.
|
LC System: |
ACQUITY UPLC System |
|
Column: |
ACQUITY UPLC BEH HILIC 2.1 x 100 mm, 1.7 μm Column |
|
Column temp.: |
35 °C |
|
Flow rate: |
700 μL/min |
|
Mobile phase: |
10 mM ammonium acetate in 90/10 acetonitrile/water |
|
Injection volume: |
5 μL |
|
ACQUITY PDA: |
200–300 nm |
|
MS System: |
ACQUITY TQD |
|
Software: |
MassLynx v.4.1 |
|
Ionization mode: |
ESI positive (melamine and ammeline) ESI negative (cyanuric acid) |
|
Capillary voltage: |
3 kV |
|
Desolvation gas: |
Nitrogen, 900 L/Hr |
|
Cone gas: |
Nitrogen, 50 L/Hr |
|
Source temp.: |
150 ˚C |
|
Desolvation temp.: |
400 ˚C |
|
Acquisition: |
Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM) |
|
Collision Gas: |
Argon at 3.5 x 10-3 mBar |
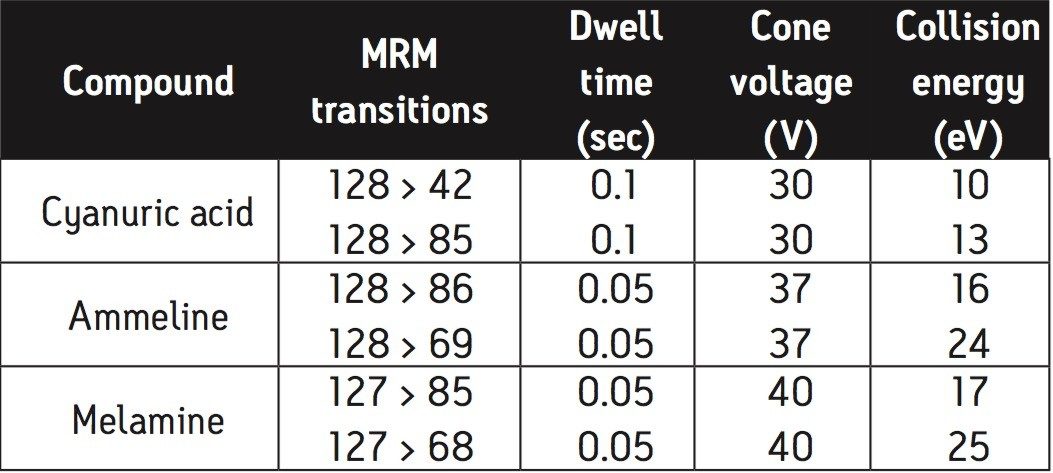
Two Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM) transitions were monitored for each compound. The primary transition is used for quantification and the secondary transition is used for confirmation purposes. The MRM transitions, dwell times, optimized collision energies and cone voltages are shown in Table 1.
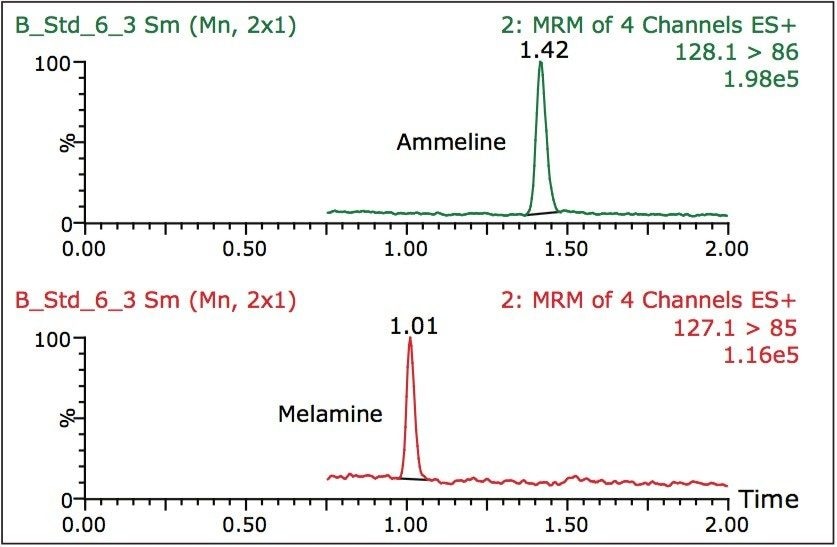
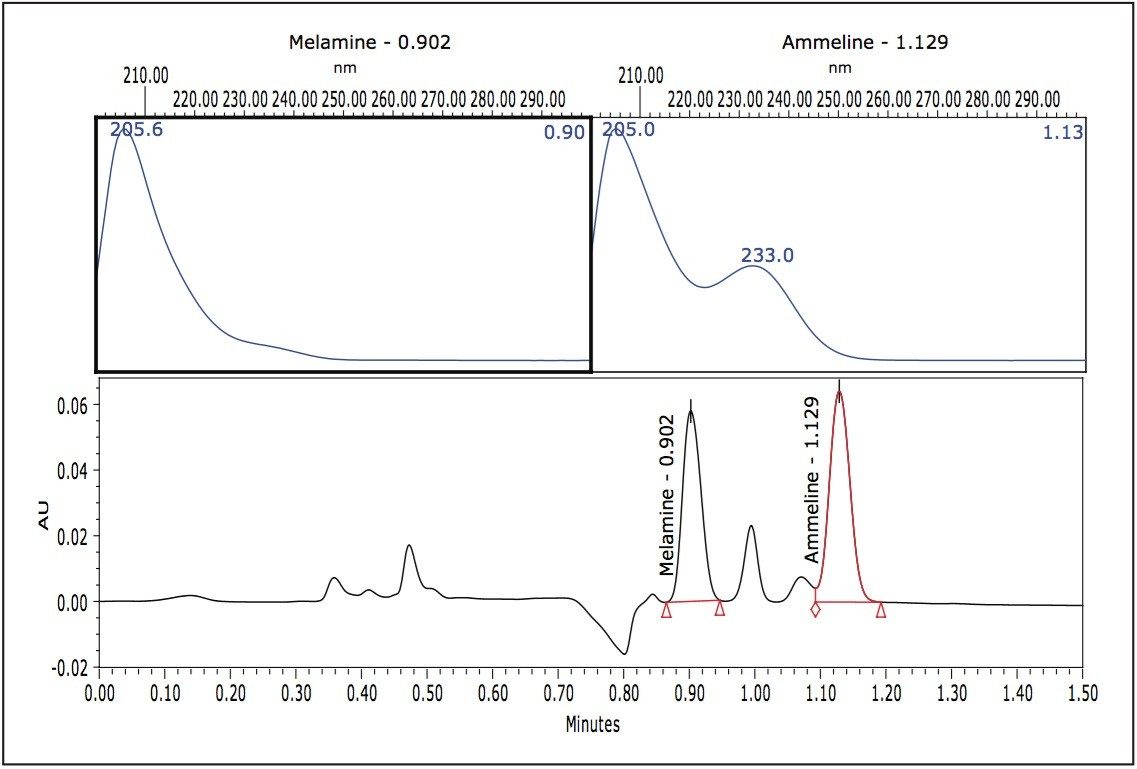
Melamine and ammeline were separated and confirmed in less than 1.5 minutes using ACQUITY UPLC with the TQD benchtop tandem quadrupole mass spectrometer. See Figure 3. The ACQUITY UPLC BEH HILIC Column provided good peak shapes enabling confident quantification of pet food and gluten type samples. For the analysis of tissue samples, an isotopically labeled internal standard is typically necessary for accurate quantification. This communication does not illustrate tissue analyses as isotopically labelled internal standards are not currently available for these compounds.
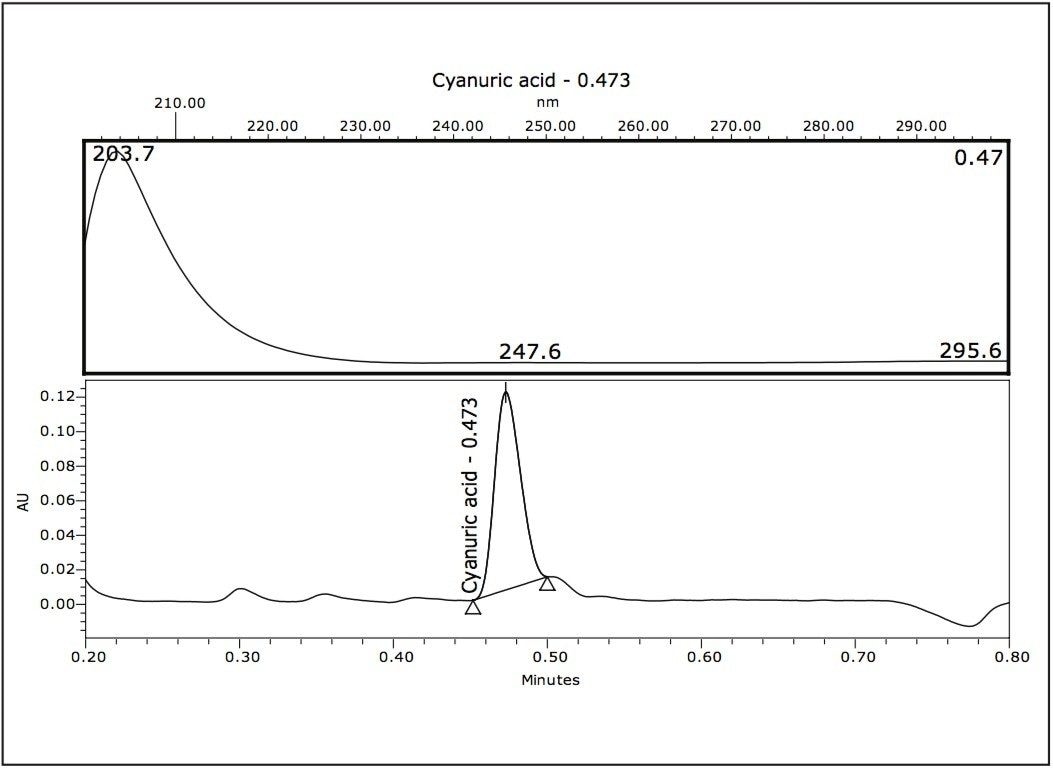
Cyanuric acid was analyzed in a separate run using the same chromatographic conditions as those used for the melamine and ammeline analysis. A UPLC-MS/MS chromatogram of cyanuric acid is shown in Figure 4.
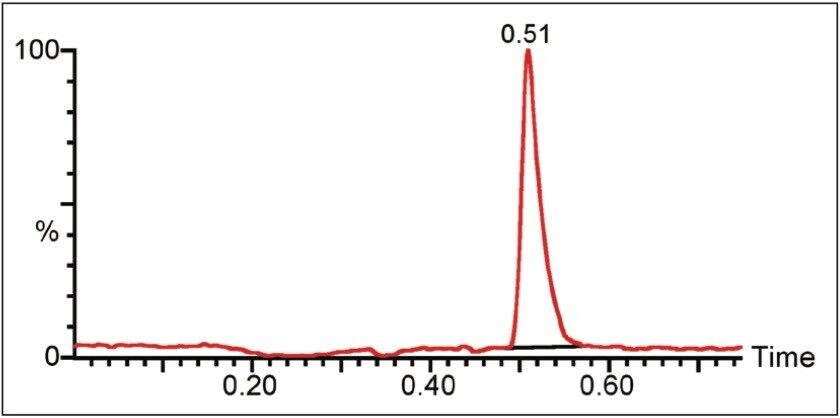
Figure 5 shows an extracted dry dog food sample spiked with melamine and ammeline. Waters TargetLynx Application Manager Software, which automates data processing and reporting for quantitative results, provided confirmation of the presence of melamine and ammeline by calculating the ion ratio between the primary and secondary MRM transitions for each compound. The TargetLynx browser for ammeline is shown in Figure 6.
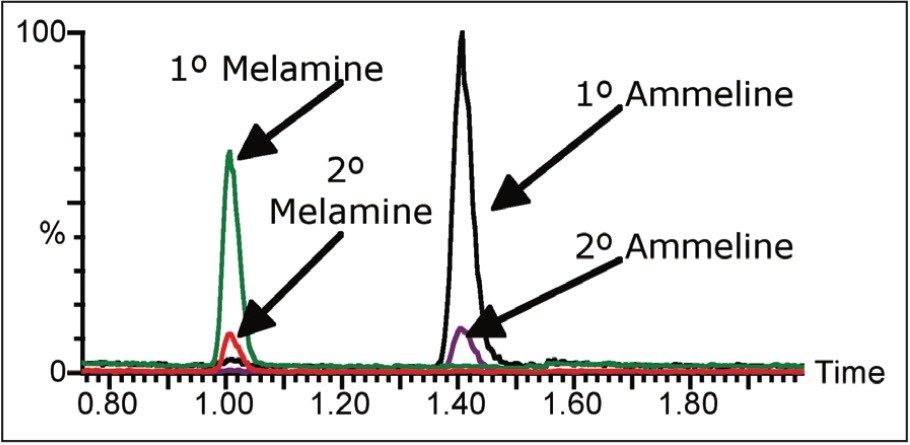
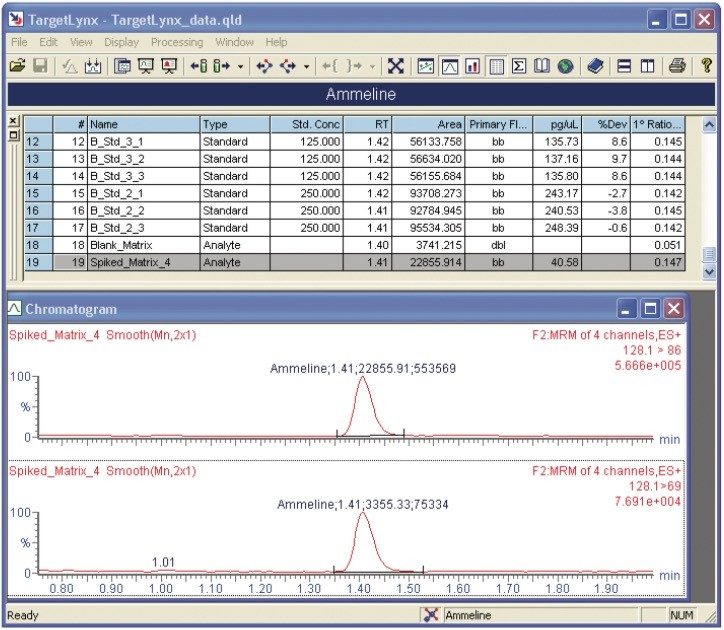
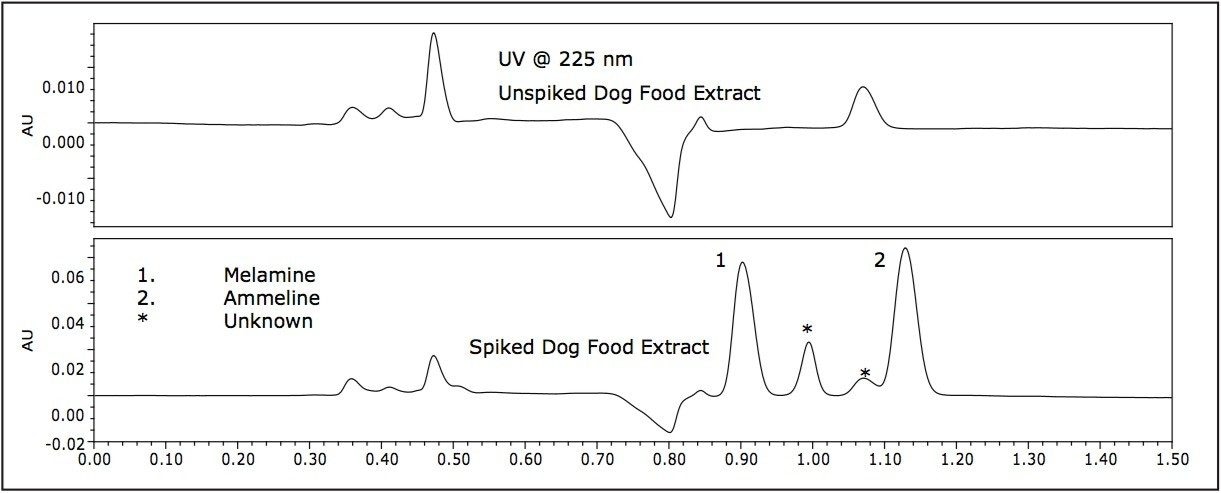
Figure 7 is a representative separation of melamine and ammeline spiked pet food in less than 1.5 minutes using ACQUITY UPLC with PDA detection. The separation uses the same ACQUITY BEH HILIC 2.1 x 100 mm Column and mobile phase composition as thetandem quadrupole MS method. Calibration curves for both compounds were found to be linear over the range 1–25 ppm.
The melamine and ammeline peaks can be easily identified by retention time and integrated for quantification. The unknown peak at one minute in Figure 7 has a lambda max at 221 nm. A peak of similar RT and lambda max is found when a pure ammeline standard is run and is therefore thought to be an impurity in the ammeline. The second unknown peak next to ammeline peak has a lambda max at 236 nm and is similar to the peak in the unspiked dog food.
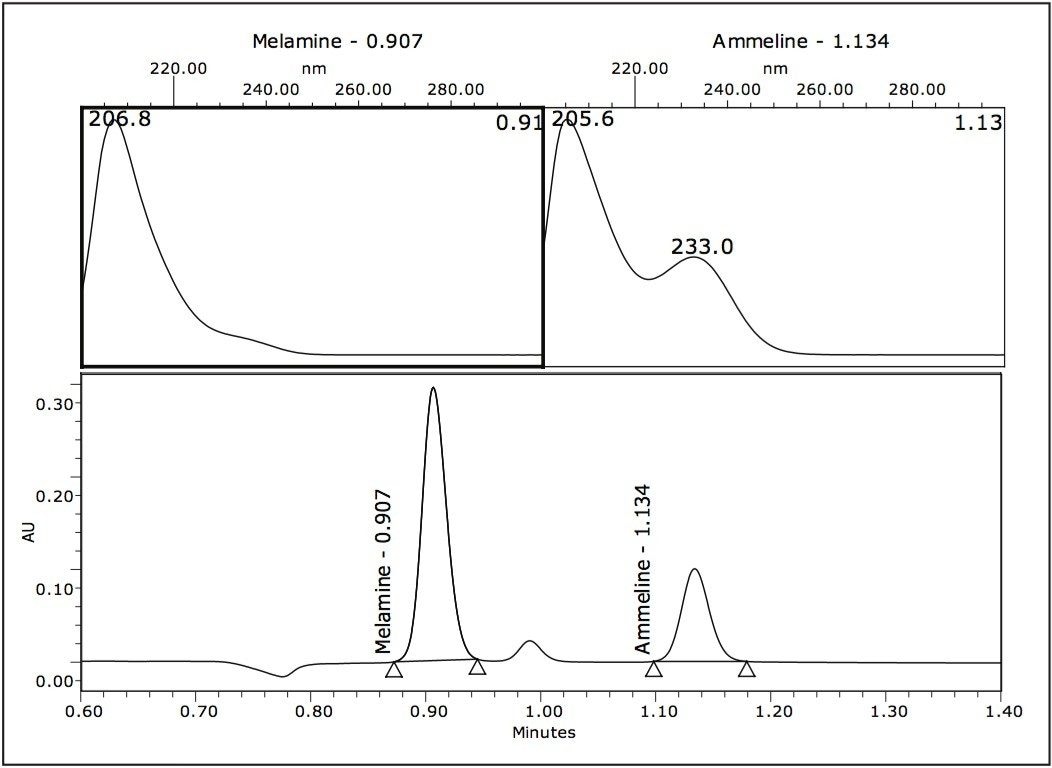
Confidence in component identification can be increased beyond simple retention time matching by using UV spectral library functions with PDA and Empower Software. Figures 8 and 9 show the spectrum index plot for 10 ppm standards of melamine and ammeline and cyanuric acid respectively. A spectrum index plot, confirming the spectral match for melamine and ammeline in a spiked pet food sample is shown in Figure 10.
In less than two minutes, the ACQUITY UPLC with the benchtop tandem quadrupole mass spectrometer, TQD, provides enhanced sensitivity and mass specificity that allows quantifiable detection of melamine and ammeline at ppb levels. Confirmation was achieved in spiked dog food using a secondary ion MRM transition for melamine and ammeline. Cyanuric acid was analyzed in a separate chromatographic run due to the risk of formation of melamine - cyanuric acid crystals.
ACQUITY UPLC PDA detection provides a rapid, cost-effective alternative to UPLC-MS/MS when enhanced sensitivity and mass specificity are not needed. The ability to quickly analyze for melamine and metabolites can facilitate workflow related to QC or regulatory compliance of products.
720002300, September 2007