For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
A rapid method for quantification of 17-OHP, cortisol, and A4 was developed using UPLC-MS/MS. Using MRM qualifier and quantifier ion transition ratios allows analytical sensitivity with added confidence in compound identity when clinical research requires a high level of analytical selectivity. The research method demonstrates good linearity, analytical sensitivity, and precision. The selectivity of the UPLC method enables chromatographic resolution of isobars for added confidence in the measured result.
Measurement of 17-hydroxyprogesterone (17-OHP) by immunoassay is prone to analytical interference arising from cross-reactivity of reagent antibodies with structurally-related steroid metabolites. A method for the extraction and UPLC-MS/MS analysis of serum 17-OHP and two additional adrenal steroids, androstenedione (A4) and cortisol, using the ACQUITY UPLC System with the Xevo TQ MS (Figure 1) is described.

Calibrators and quality-control material (QC) were prepared in double charcoal-stripped serum over the stated measurement range. Samples, 50 μL and 20 μL, of internal standard ([2H8] 17-OHP, [2H7] A4, and [2H4] cortisol) were extracted into 1 mL of methyl-tert-butyl-ether. The evaporated organic layer (800 μL) was reconstituted in 50 μL 45% (v/v) methanol (aq).
|
System: |
ACQUITY UPLC |
|
Sample preparation vials: |
TruView LCMS Certified Maximum Recovery Vial (p/n 186005662CV) |
|
Column: |
ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3, 1.8 μm, 2.1 x 50 mm (p/n 186003538) with an ACQUITY HSS T3, VanGuard Pre-column, 1.8 μm, 2.5 x 5 mm (p/n 186003976) |
|
Column temp.: |
60 °C |
|
Sample temp.: |
8 °C |
|
Injection volume: |
20 μL |
|
Flow rate: |
600 μL/min |
|
Injection mode: |
Partial loop, with needle overfill (PLNO); Load ahead feature enabled (5 min injection-to-injection) |
|
Mobile phase A: |
2 mmol/L ammonium acetate, 0.1 % (v/v) formic acid (aq) |
|
Mobile phase B: |
2 mmol/L ammonium acetate, 0.1 % (v/v) formic acid in methanol |
|
Gradient (binary system): |
Initial conditions of 45% mobile phase B were increased linearly to 47% over 1 minute and then, over an additional minute, to 57%. Thereafter, mobile phase B was again increased, this time to 98% over 0.5 minutes. The composition was then maintained at 98% B for 0.5 minutes before reverting to 45% B followed by column re-equilibration for 1.5 minutes. The overall run time was 4.5 minutes. |
|
System: |
Xevo TQ (0.7 FWHM on MS1 and 0.8 FWHM MS2) |
|
Ionization mode: |
Electrospray positive |
|
Capillary voltage: |
0.7 kV |
|
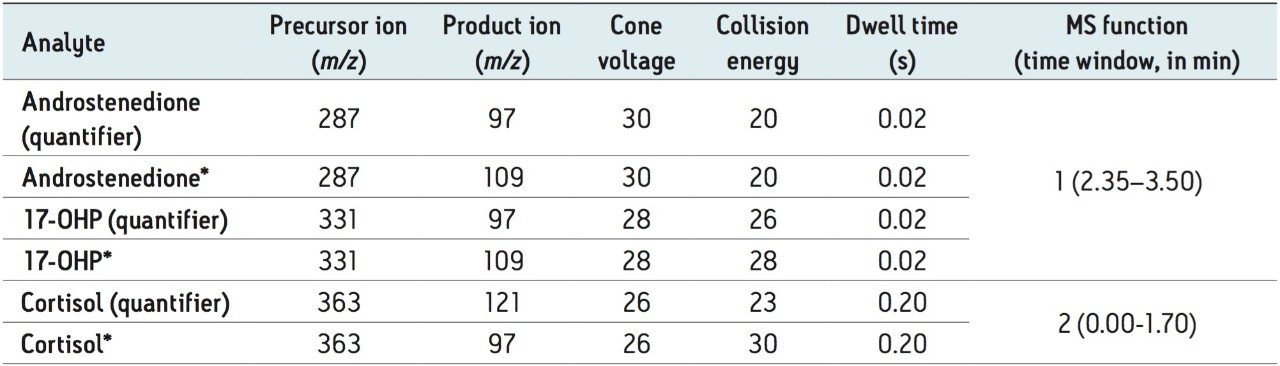
Collision energy: |
Analyte specific (see Table 1) |
|
Cone voltage: |
Analyte specific (see Table 1) |
MassLynx Software v4.1 with TargetLynx Application Manager
The limit of detection (LOD) and lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) were determined as the lowest concentration of steroid spiked into charcoal-stripped serum to produce a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) >3 or >8, respectively. The LLOQ was confirmed by demonstrating ≤15% imprecision and deviation from assigned values following replicate analysis (n =10), a percentage value that surpasses the imprecision targets of ≤20% CV prescribed by the United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) in its Guidance for Industry.1 The LOD and LLOQ were 0.25 and 0.5 ng/mL, respectively, for all analytes. Mass (ng/mL) to nanomolar-unit conversion factors are x3.03 for 17-OHP, x2.76 for cortisol, and x3.49 for A4.
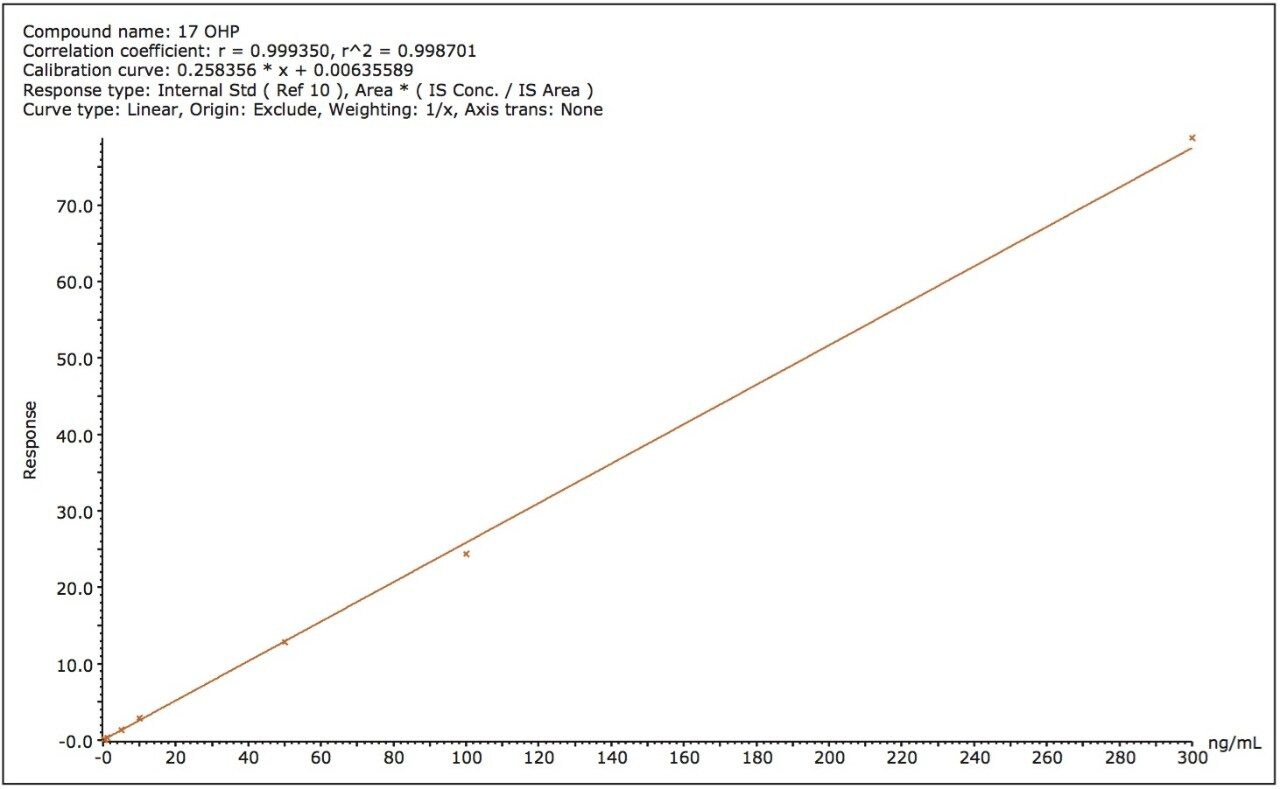
The correlation between analyte concentration and response ratio was linear from the LLOQ to 300, 500, and 200 ng/mL for 17-OHP, cortisol, and A4, respectively. The coefficient of determination (r2) for all analytes was >0.997. Figure 2 shows a calibration curve for 17-OHP. Calculated concentrations of calibrators were ≤10% of assigned values, with the exception of the lowest concentration calibrator at the LLOQ, for which a deviation of ≤15% from the nominal value was accepted.
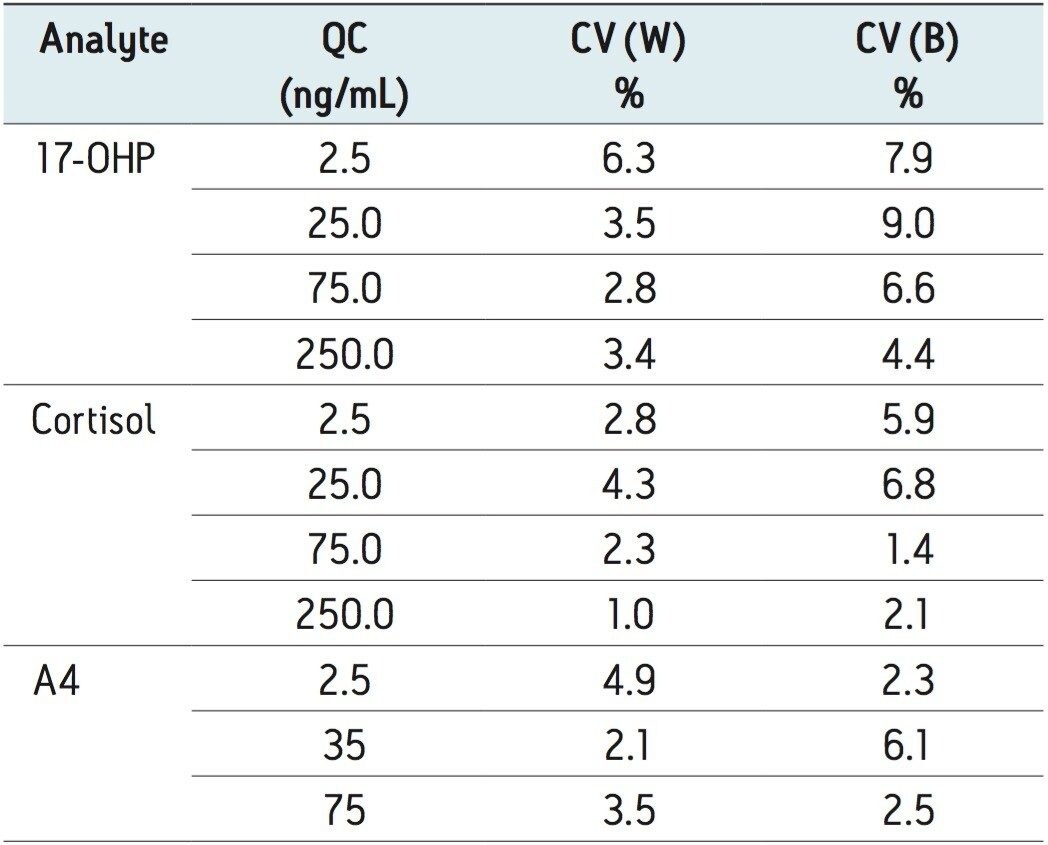
The within-batch imprecision was determined from replicate (n = 5) analysis of multiple levels of QC. The maximum between-batch imprecision was evaluated by replicate (n = 5) analysis of the QC over five consecutive days. The findings are summarized in Table 2. The determined concentrations were <7.5% of nominal values.
Recovery was evaluated as the ratio of detector response in pre- to post-extraction-spiked serum samples. Recovery was calculated as >70% for all steroids. The magnitude of electrospray ionization suppression from residual sample interferences was estimated by calculation of the matrix factor for each analyte. The matrix factor was defined as the mean ratio of the peak-area response in presence to absence of residual sample matrix (n = 6, human whole serum). These studies indicated approximately 10% of the detector signal for cortisol and A4, with 50% of the signal for 17-OHP was suppressed by residual matrix ions. The use of stable isotope-labeled internal standards compensated for the observed matrix effects.
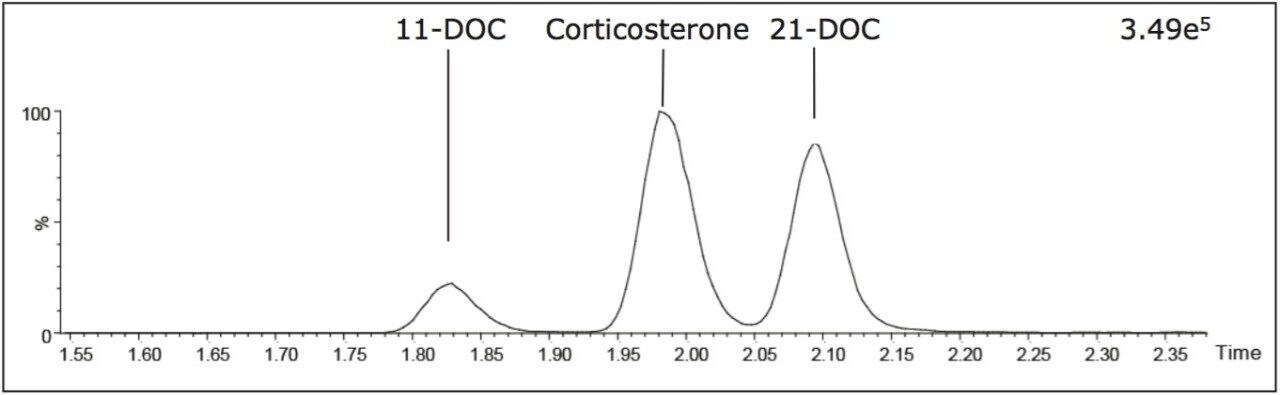
Further interference studies were conducted whereby serum was supplemented with a selection of adrenal steroid intermediates, extracted and analyzed by the UPLC-MS/MS method described herein. A subset of intermediates, isobaric for the MRM transition 347 > 121 were identified, namely: 11- and 21-deoxycortisol and corticosterone. Inspection of the total-ion chromatograms of the three isobars showed these steroids were resolved from one another (Figure 3). Interferences were not observed at or around the retention time of the compounds of interest in the 347 > 121 total-ion chromatograms, confirming the analytical selectivity for the detection of 17-OHP, cortisol, and A4 with respect to the subset of steroid intermediates described herein.
A rapid method for quantification of 17-OHP, cortisol, and A4 was developed using UPLC-MS/MS. Using MRM qualifier and quantifier ion transition ratios allows analytical sensitivity with added confidence in compound identity when clinical research requires a high level of analytical selectivity. The research method demonstrates good linearity, analytical sensitivity, and precision. The selectivity of the UPLC method enables chromatographic resolution of isobars for added confidence in the measured result.
720005215, December 2014