Simultaneous Determination of Naphazoline Hydrochloride and Pheniramine Maleate along with their Related Compounds by High Performance Liquid Chromatography on an Alliance™ iS HPLC System
Abstract
In this study, a liquid chromatographic method was developed for simultaneous determination of two active ingredients - naphazoline hydrochloride and pheniramine maleate ophthalmic, along with their related compounds. The method achieved complete separation of analytes within 20 minutes, in a single run at a temperature of 40 °C and a flow rate of 2.0 mL min−1, using an XSelect™ CSH C18 Column. A comprehensive evaluation of system suitability, range, accuracy (recovery), intraday and interday precisions was performed as a part of this study. The method was also found to be linear in the range of 80 to 120% with respect to the API concentration in a working concentration, displaying a correlation coefficient (R2) greater than 0.997. As a practical application, the method was successfully used for the routine analysis of commercially available ophthalmic and nasal solutions, without significant interference from the excipients.
Benefits
This single HPLC method using the XSelect CSH C18 Column in combination with the Alliance iS HPLC System can replace several separate methods for the analysis of assays and organic impurities of naphazoline hydrochloride and pheniramine maleate active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
Introduction
Naphazoline is an active pharmaceutical compound that helps to relieve eye redness and puffiness by acting as a decongestant and vasoconstrictor. Pheniramine maleate, on the other hand, is an antihistamine commonly used to alleviate temporary symptoms caused by the common cold, flu, allergies, or other respiratory illnesses. These two active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are often combined in eye drops to provide relief for allergic conjunctivitis, including hay fever.[1, 2] To ensure compliance with regulatory requirements for pharmaceutical composition, dosage, and purity, it is crucial to analyze the contents of such medications for quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) purposes.
In recent years, the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) has undertaken a modernization effort to update outdated analytical methodologies in its monographs. This initiative aims to provide updated public standards and reinforce regulatory agencies' efforts to safeguard public health. The focus is on the main sections of monographs, which include identification, assay, and organic impurities.
A key element of the modernization process is the elimination of hazardous solvents and reagents in the analytical procedure. Currently, the industry uses separate chromatographic methods to analyze each API in pharmaceutical formulations. While effective, this approach can generate large amounts of hazardous waste from organic solvents.
To minimize hazardous waste, one solution is to use a single chromatographic method to analyze multiple active materials and their related compounds. In this study, we demonstrate the combination of three USP chromatographic methods into a single LC method for analyzing two APIs (naphazoline hydrochloride and pheniramine maleate) and their related compounds.
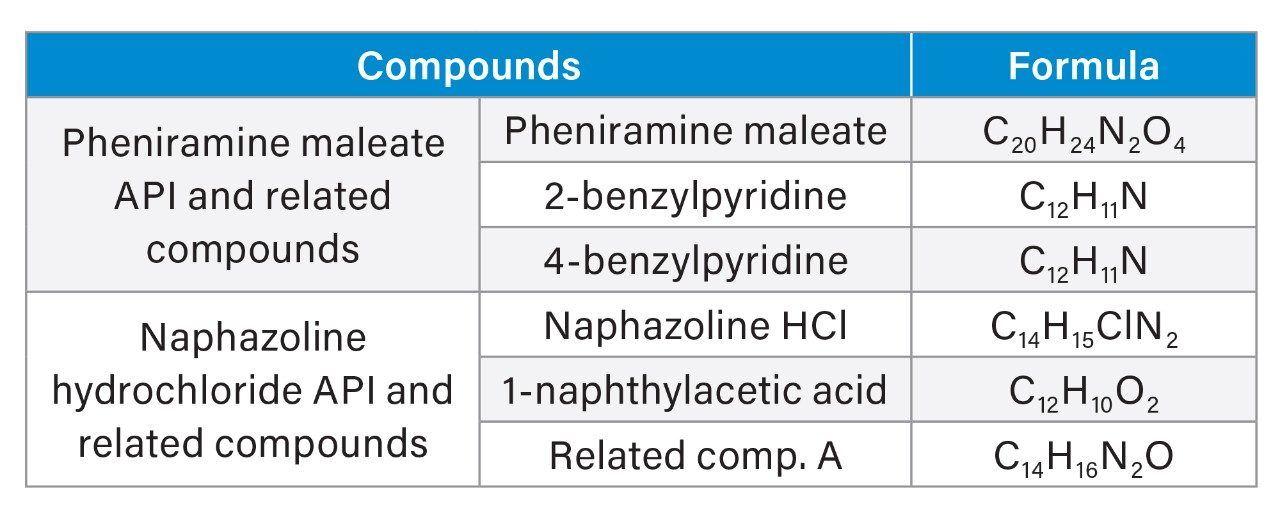
Names and chemical formulas of these analytes are detailed in Table 1.
Experimental
Pheniramine maleate and its related compounds (2-benzylpyridine, 4-benzylpyridine) were kindly provided by the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) (Rockville, MD, USA). Naphazoline HCl and its related compounds (1-naphthylacetic acid, Related comp. A) were also each provided by the USP. Standard stock solutions were prepared in diluent (90:10 mobile phase A/mobile phase B) and subsequently diluted to make a resolution mixture that contains pheniramine/naphazoline 500/40 µg/mL with 5 µg/mL related substances. All solutions were stored in PP containers in a freezer (-20 °C). Over the counter ophthalmic solutions formulations containing 0.025% (v/v) of pheniramine maleate and 0.3% v/v naphazoline HCl were purchased from a local drug store.
LC Conditions
|
LC system: |
Alliance iS HPLC System with a Tunable UV detector |
|
Detection: |
TUV (Dual Wavelength, 260, and 280 nm) |
|
Column: |
5 µm, 4.6x150 mm XSelect CSH C18 Column pH range: 2–10 |
|
Column temp.: |
40 °C |
|
Sample temp.: |
5 °C |
|
Injection volume: |
8 µL |
|
Flow rate: |
2.0 mL min-1 |
|
Mobile phase A: |
0.05% (v/v) triethyl amine and 0.05% (v/v) phosphoric acid in water (non pH adjusted) |
|
Mobile phase B: |
0.05% (v/v) phosphoric acid in Acetonitrile |
|
Gradient profile: |
Initial hold of 6 minutes at 5% organic and 95% aqueous followed by a linear gradient of organic from 5–95% over 7 minutes. |
Data Management
|
Chromatography software: |
Empower™ 3 Chromatographic Data System |
Results and Discussion
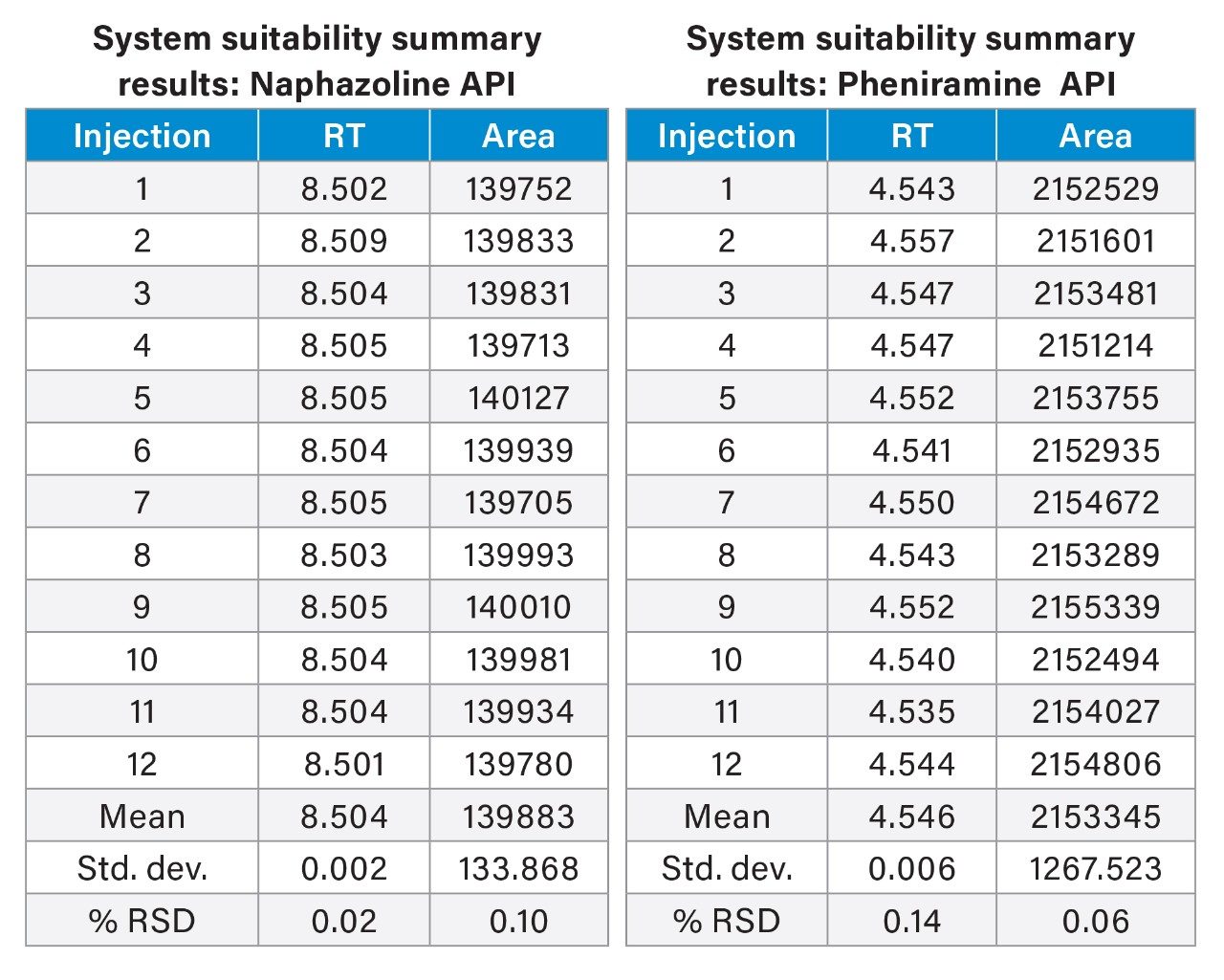
To verify the functionality of the chromatographic system, it was important to perform System Suitability Testing (SST). SST is a standard procedure used to verify the efficiency and repeatability of a chromatographic system to ensure its suitability for a specific analysis. To demonstrate this, the system underwent 12 replicate injections of the SST working standard (500/40 µg/mL of pheniramine maleate/naphazoline HCl), and the results, presented in Table 2, showed that the relative standard deviation (%RSD) for the peak areas of naphazoline and pheniramine was less than 0.1 for 12 consecutive injections. The %RSD for the retention time for these two peaks was 0.02 for pheniramine and 0.14 for naphazoline. These findings indicate that the developed method and the system offer outstanding repeatability of retention times and peak areas.
Linearity of APIs
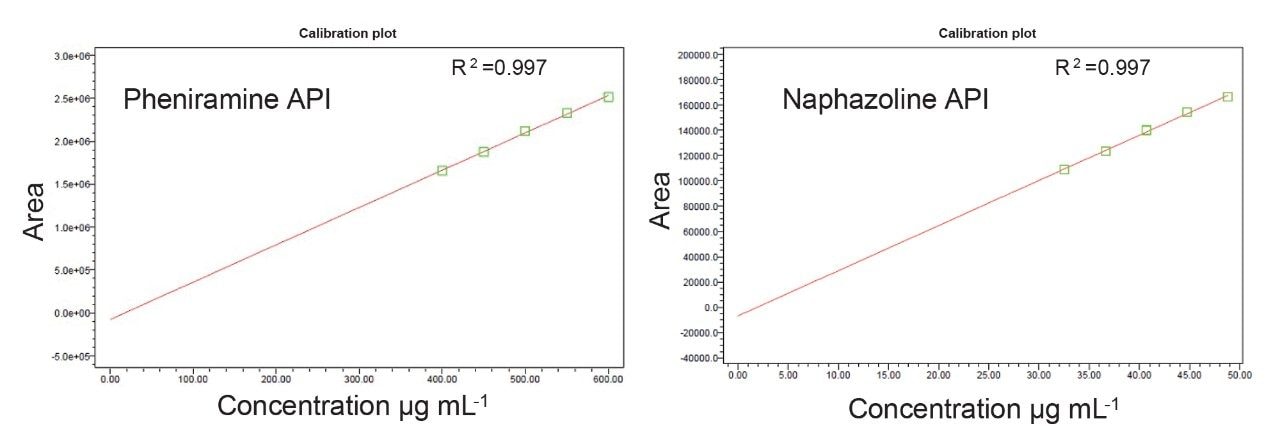
Assessing the linearity of a chromatographic method is crucial for accurate and reliable quantification of analytes across a broad range of concentrations. A calibration curve is typically established by testing the same analyte at various concentrations to determine its concentration in unknown samples. In this study, linearity was assessed by preparing five mixtures at concentrations ranging from 80% to 120% of the target concentration of 500/40 µg/mL of pheniramine maleate/naphazoline HCl. Each solution was then injected in duplicate into the chromatographic system, and the response area was recorded. The resulting linear calibration curves were constructed by plotting peak area against concentration, and regression equations were computed, indicating a strong correlation coefficient (R2) greater than 0.997, as shown in Figure 1.
Related Compounds
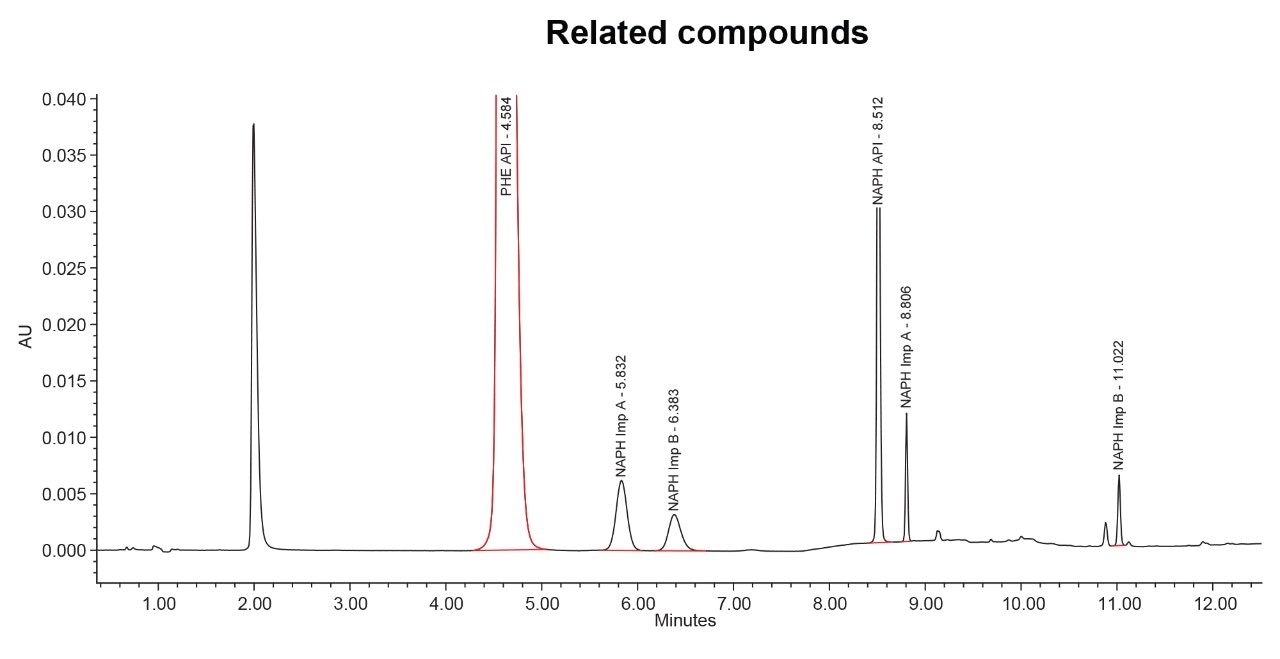
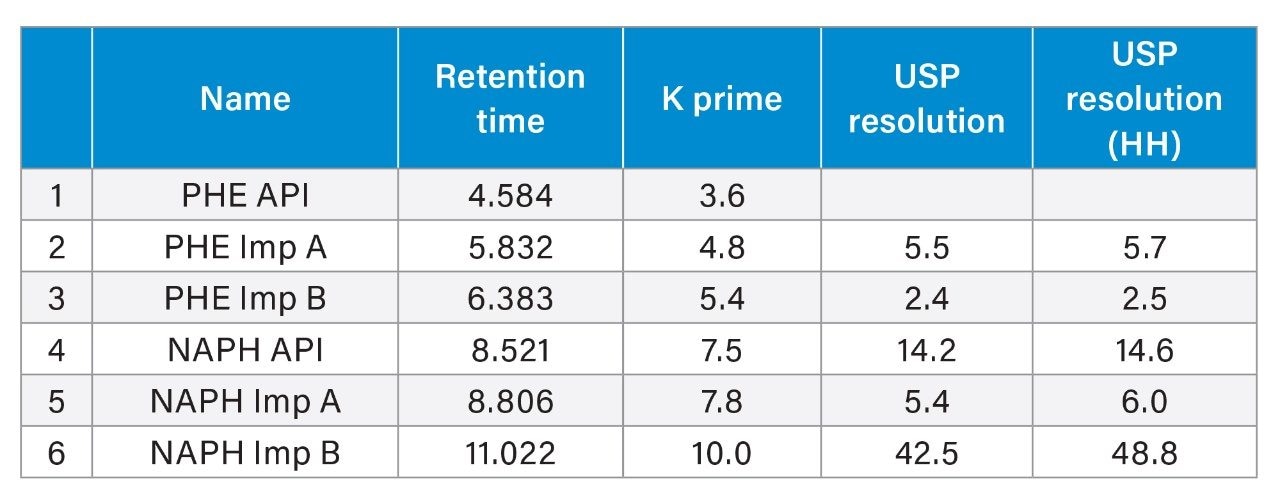
The ability of an analytical method to separate related compounds from API peaks is of critical importance to ensure that the drug is safe, effective, and stable. To assess the developed method’s capability in separating the active ingredients from their related compounds, it was interesting to run the method on a standard Resolution Mixture that contains naphazoline hydrochloride/ pheniramine maleate and their related compounds. The obtained results demonstrated that the method effectively separated all the compounds in the mixture, with a minimum USP resolution of 2.4, as depicted in Figure 2 and Table 3.
Intra-day and inter-day Precisions
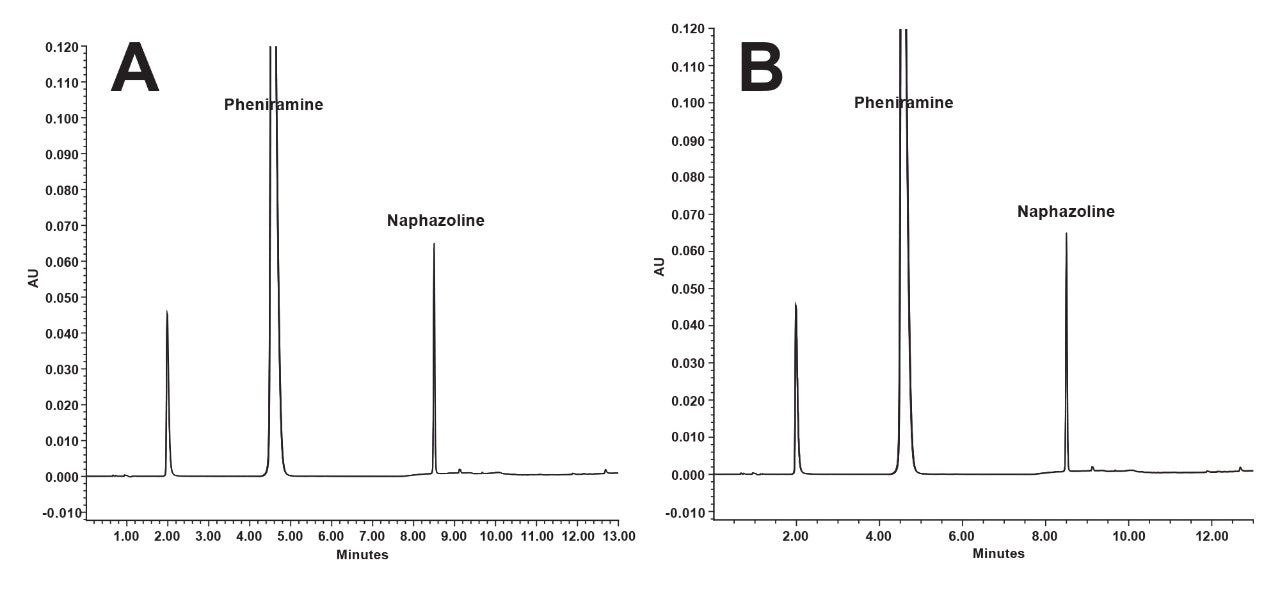
Precision refers to the level of agreement among individual results when the procedure is repeatedly applied to several samples taken from the same homogenous sample. Intra-day precision of the method was evaluated by performing 12 replicate injections of the system suitability mixture as previously demonstrated in the system suitability section. For inter-day precision, the same samples were analyzed in two different days (12 replicate injections on day one and additional five replicate injections on the second day). Results revealed that the %RSD for the peak area and the retention time of Pheniramine over the 17 replicate injections was 0.15 and 0.58 respectively. Similar results were also observed for Naphazoline of %RSD values of peak area and retention time of 0.03 and 0.59 respectively. The results indicate that the method has good precision for detection of targeted compounds and %RSD below 0.6% confirming that the method is sufficiently precise. Overlay chromatograms of the 12 and the 17 injections are displayed in Figure 3.
Analysis of Ophthalmic and Nasal Solutions
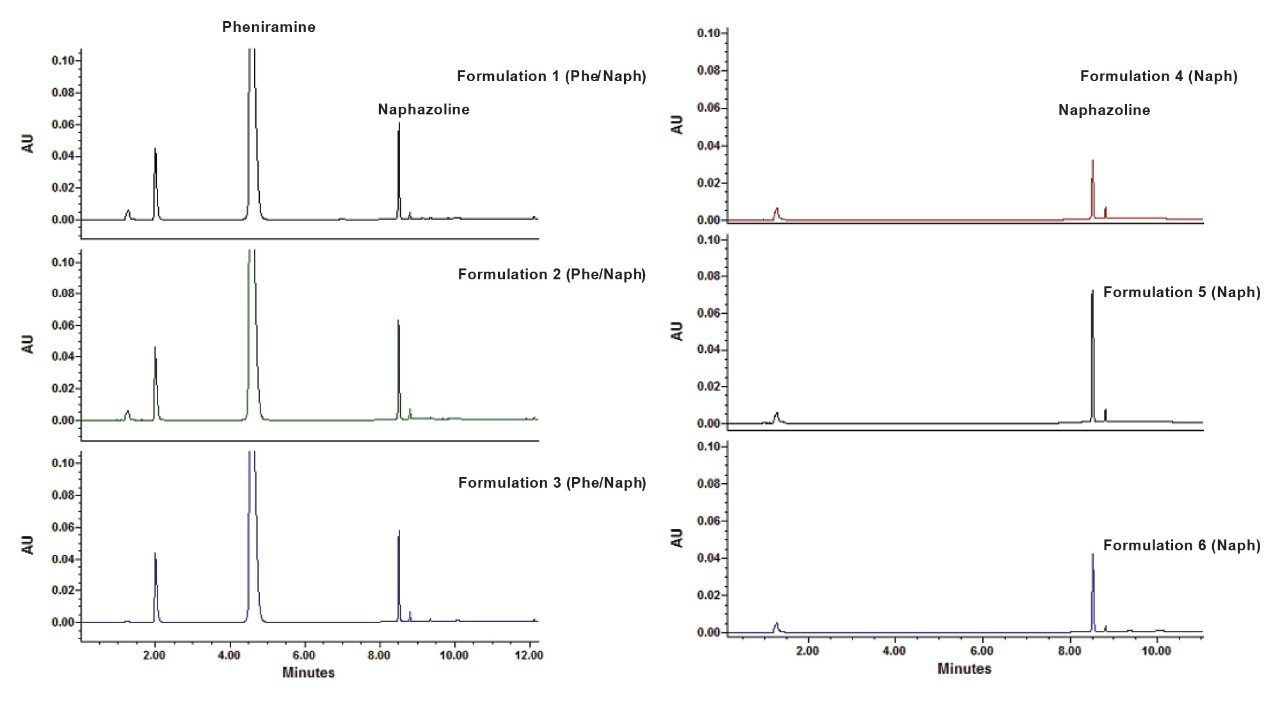
Application of the method to the analysis of samples obtained from commercially available ophthalmic and nasal solutions was then performed. The samples were prepared as follows: the solutions were diluted in the diluent (90:10 mobile phase A/mobile phase B) to the working concentrations of 500 µg/mL pheniramine maleate/40 µg/mL naphazoline HCl for formulas 1, 2, and 3 eye allergy relief solutions and 40 µg/mL naphazoline HCl for formulas 4, 5, and 6 redness and cooling eye drops . Results showed that the developed method was successful at meeting the USP monographs’ criteria for assay recoveries to be within 90–110% for both APIs (pheniramine (PHE) and naphazoline (NAP))[3–5]. Representative separations of four different drug formulations are represented in Figure 4.
Conclusion
- A single LC method, specific for analysis of active ingredients and their related compounds was developed to combine three USP monographs for naphazoline HCl and pheniramine maleate ophthalmic and nasal solutions.
- Alliance iS HPLC System enabled rapid and reliable separation of multiple APIs along with their related compounds in a single HPLC method.
References
- A. Uncini, G. De Nicola, A. Di Muzio, G. Rancitelli, L. Colangelo, D. Gambi, P.E. Gallenga, Topical Naphazoline in Treatment of Myopathic Ptosis, Acta Neurol Scand 87(4) (1993) 322–4.
- L. Quan, H. He, Treatment With Olopatadine and Naphazoline Hydrochloride Reduces Allergic Conjunctivitis in Mice Through Alterations in Inflammation, NGF and VEGF, Mol Med Rep 13(4) (2016) 3319–3325.
- USP Monograph, Naphazoline Hydrochloride Nasal Solution, USP40-NF35, The United States Pharmacopeia Convention, official December 2017.
- USP Monograph, Naphazoline Hydrochloride Ophthalmic Solution, USP40-NF35, The United States Pharmacopeia Convention, official December 2017.
- USP Monograph, Naphazoline Hydrochloride and Pheniramine Maleate Ophthalmic Solution, USP40-NF35, The United States Pharmacopeia.
Featured Products
720007876, March 2023