
This is an Application Brief and does not contain a detailed Experimental section.
This application brief demonstrates reliable quantification of six nitrosamine impurities (NDMA, NDEA, NEIPA, NDIPA, NDBA, and NMBA) in valsartan and NDMA in ranitidine by UV detection, with the added benefit of mass confirmation by mass spectral data using an ACQUITY QDa Mass Detector.
The ACQUITY Arc System with PDA Detector, integrated with an ACQUITY QDa Mass Detector for accurate mass confirmation, enables reliable quantification of nitrosamine impurities in valsartan and ranitidine drug substances.
Carcinogenic impurities, such as nitrosamines, can cause DNA mutations, potentially leading to cancer.1 Several medications containing valsartan or ranitidine drug substances have been recalled due to the presence of nitrosamine impurities in the final drug products.1,2 Due to their high toxicity, these impurities must be monitored at low levels using reliable methods to ensure safety of the pharmaceutical products.
In this work, we present an HPLC method with UV detection for the simultaneous quantification of six nitrosamine impurities in valsartan drug substance, including N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), N-nitroso-N-methyl-4-aminobutyric acid (NMBA), N-nitrosodiethylamine (NDEA), N-nitrosoethylisopropylamine (NEIPA), N-nitrosodiisopropylamine (NDIPA), and N-nitrosodibutylamine (NDBA). This method also enables analysis of NDMA in ranitidine drug substance. The achievable quantitation limits for nitrosamine impurities using UV detection range from 10–20 ng/mL, with method linearity over 10–1000 ng/mL producing R2 ≥0.999. The mass spectral data from an ACQUITY QDa Mass Detector was used for quick and accurate peak identity confirmation.
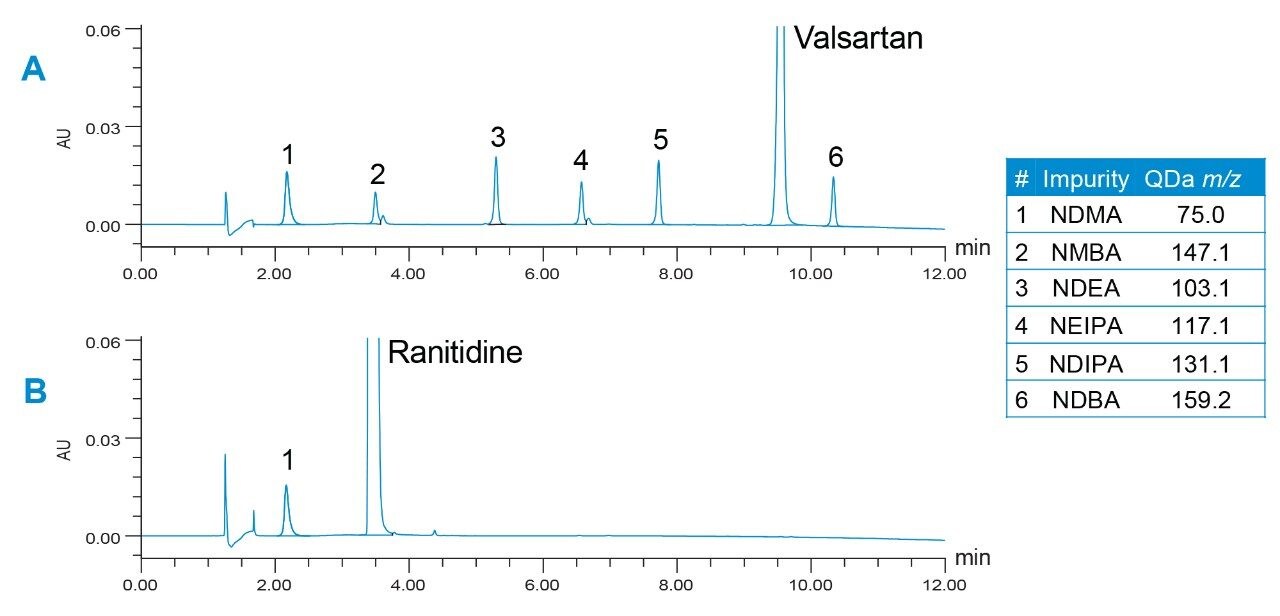
The HPLC separation was performed using an XSelect HSS T3 Column, based on a previously described method.4 The conditions of the method were modified to achieve optimal UV performance for nitrosamine impurities in valsartan and ranitidine drug substances. The optimized method (Table 1) provided excellent retention for nitrosamines and separation from the drug substances (Figure 1). While the UV data was used for quantitation, the mass spectral data from an ACQUITY QDa Mass Detector enabled peak identity confirmation by mass detection.
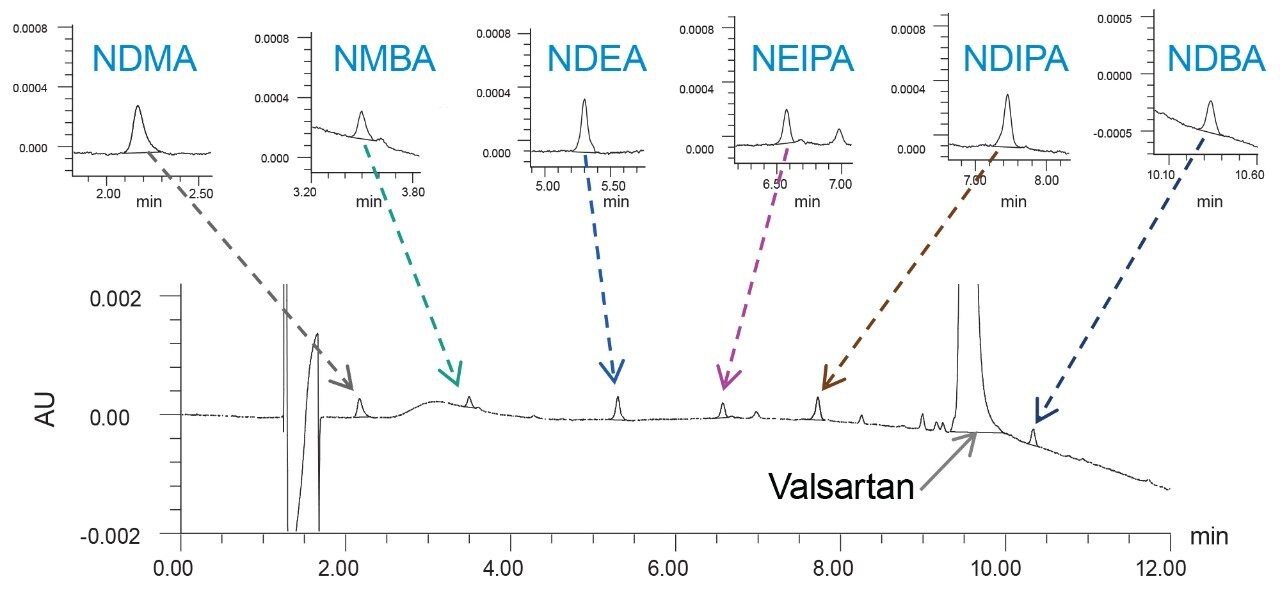
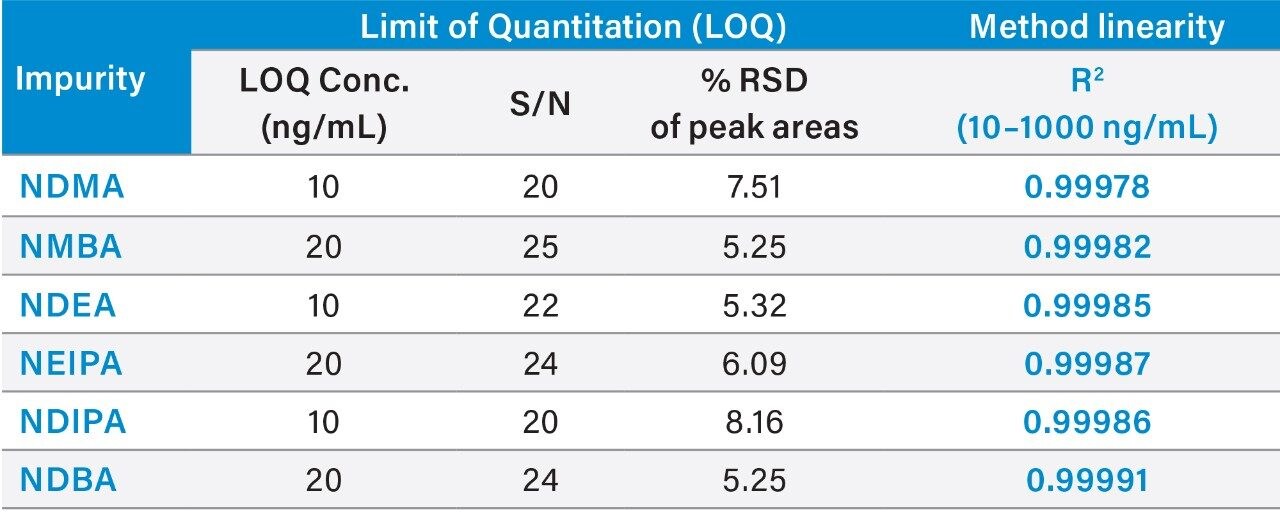
The limit of quantitation (LOQ) for nitrosamine impurities achievable with UV was determined using the signal-to-noise criteria of 10:1. The LOQ solutions were prepared by spiking ~100 μg/mL of drug substance sample in 80:20 water/methanol diluent with the nitrosamines’ standards. The LOQ was found to be 10 ng/mL for NDMA, NDEA, and NDIPA, and 20 ng/mL for NMBA, NEIPA, and NDBA, respectively. The LOQ solution at 20 ng/mL of nitrosamines in ~100 μg/mL valsartan is shown in Figure 2. Data from six replicate injections was evaluated to demonstrate performance at the LOQ level (Table 2). The %RSD of the peak areas for six replicate injections of the LOQ solutions was ≤7.51%. The method exhibited a linear response over the 10–1000 ng/mL range with correlation coefficients (R2) of >0.999 (Table 2). Data was analyzed using Empower 3 Chromatography Data System (CDS) Software.
A single HPLC/UV method was successfully developed for the reliable quantification of six nitrosamine impurities (NDMA, NMBA, NDEA, NEIPA, NDIPA, and NDBA) in valsartan and NDMA in ranitidine drug substances, with quantitation limits ranging from 10–20 ng/mL. The analysis was performed on the ACQUITY Arc System with 2998 PDA Detector, integrated with an ACQUITY QDa Mass Detector for quick and accurate peak identity confirmation. Additionally, the XSelect HSS T3 Column, a proprietary reversed-phase column, provided retentivity and specificity for all analytes. This HPLC-UV method offers a starting point for the robust quantification of nitrosamines or similar compounds.
720006775, February 2019