
This is an Application Brief and does not contain a detailed Experimental section.
Waters previously developed a method for the determination of anionic polar pesticides in various food commodities based upon extraction with the established Quick Polar Pesticides method (QuPPe) from the EURL SRM in Stuttgart and LC-MS/MS using the Anionic Polar Pesticide column. This application brief shows the successful evaluation of the performance of this method by interlaboratory study using ACQUITY UPLC systems and Xevo TQ-XS tandem quadrupole mass spectrometers. QuPPe cucumber extracts were spiked with glyphosate, AMPA, glufosinate, MPPA, and ethephon and sent to eight laboratories across Europe and India. The trueness of the method was determined to be within the range of 90 to 104%. Close agreement was observed with the repeatability within each laboratory and the reproducibility between laboratories both being <7% RSD.
Although various multi-residue LC-MS/MS methods are available to analyze food for pesticide residues, polar, anionic pesticides remain a considerable challenge. The QuPPe (Quick Polar Pesticides) method1 allows the simultaneous extraction of many highly polar pesticides and their metabolites. QuPPe is typically used with LC-MS/MS instruments offering high sensitivity to deal with the significant matrix effects associated with the crude extracts (no cleanup). Previously, we have reported the use of a method based upon QuPPe and the Anionic Polar Pesticide column for the determination of anionic polar pesticides, including glyphosate, and their metabolites in various commodities.2
Interlaboratory studies play an important role in analytical chemistry to assess the performance characteristics of an analytical method. In these studies, a group of experienced laboratories received identical portions from a homogeneous and stable test sample and conducted measurements following a strictly defined protocol to assess features such as the accuracy, repeatability, and reproducibility of the method. Here, we report the results of an interlaboratory study to further evaluate the performance of this LC-MS/MS method, using the Anionic Polar Pesticide Column on ACQUITY UPLC systems with Xevo TQ-XS tandem mass spectrometers.
Laboratories were supplied with:
Laboratories were instructed to determine the concentration of the analytes of interest from replicate injections (n=5) of the spiked extract, using bracketed calibration, with the use of stable isotope analogues as internal standards as instructed for all but ethephon. Laboratories were also asked to make 15 injections of the matrix-matched standard at 0.05 mg/kg so that the stability of the chromatographic performance might be evaluated.
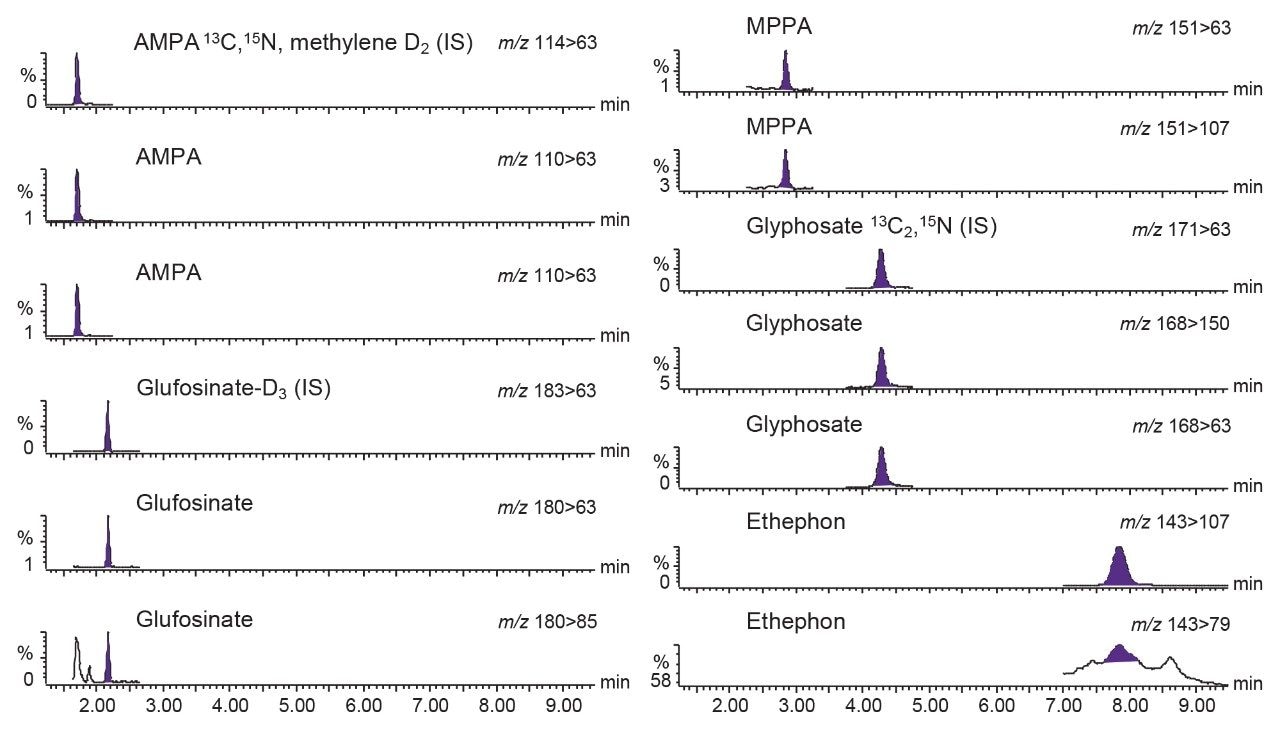
Each laboratory successfully implemented the chromatographic method so that the retention times for each compound of interest were all within 3% of the expected reference provided. The method provided retention complying with the SANTE guidelines,5 exhibited Gaussian chromatographic peak shape and good retention time stability throughout. Figure 1 shows the typical chromatography and response for the analytes at 0.01 mg/kg.
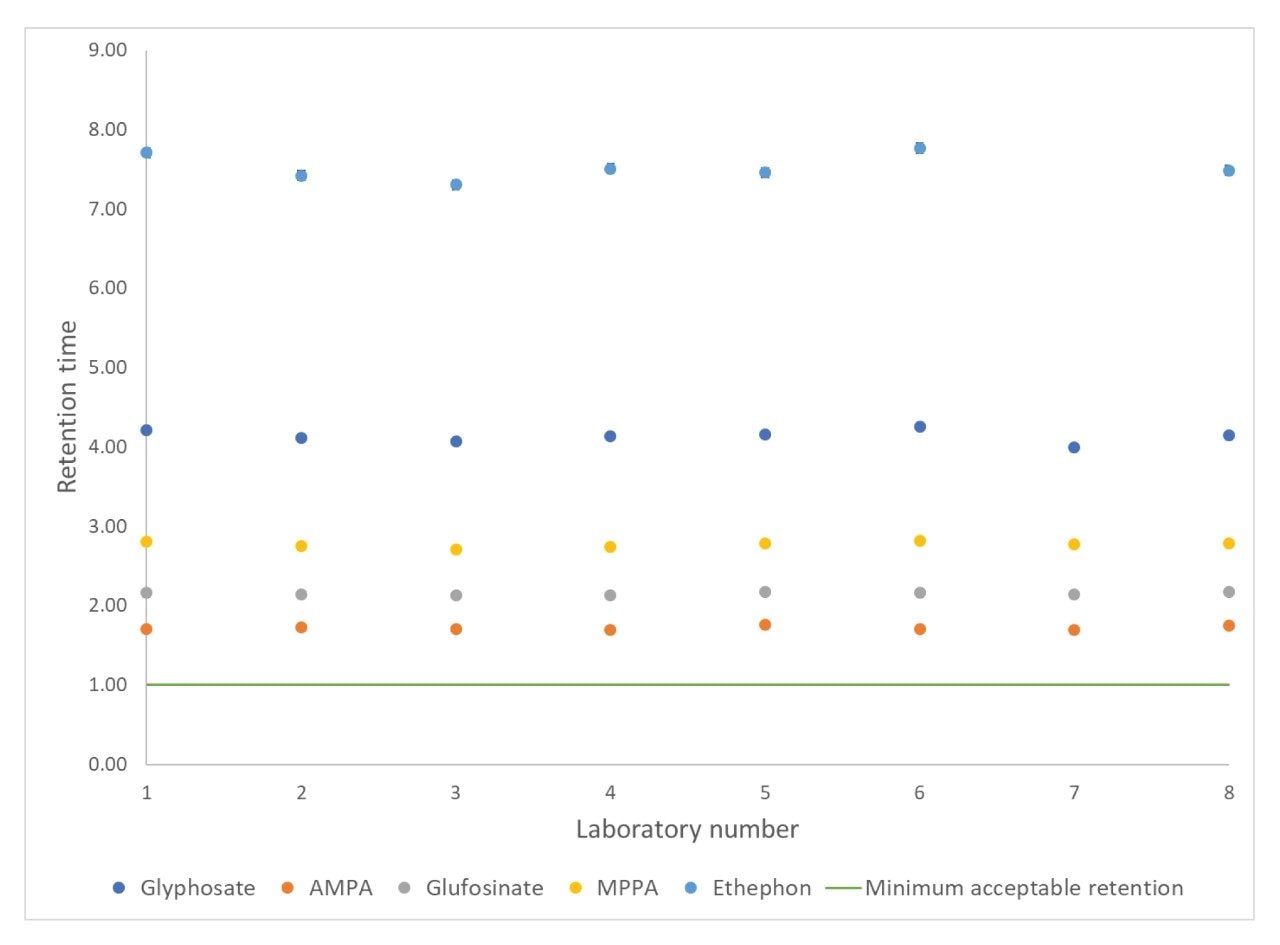
Chromatography was shown to be stable with no significant change in retention times across the 15 injections of the matrix-matched standard at 0.05 mg/kg (Figure 2). Deviation in retention times from the reference laboratory value was no greater than 0.3 minutes, showing the ease of setting up the method. Values for the repeatability of the retention time within each laboratory (RSDr) were all <0.15% and reproducibility between laboratories (RSDRL) were all <2.5%.
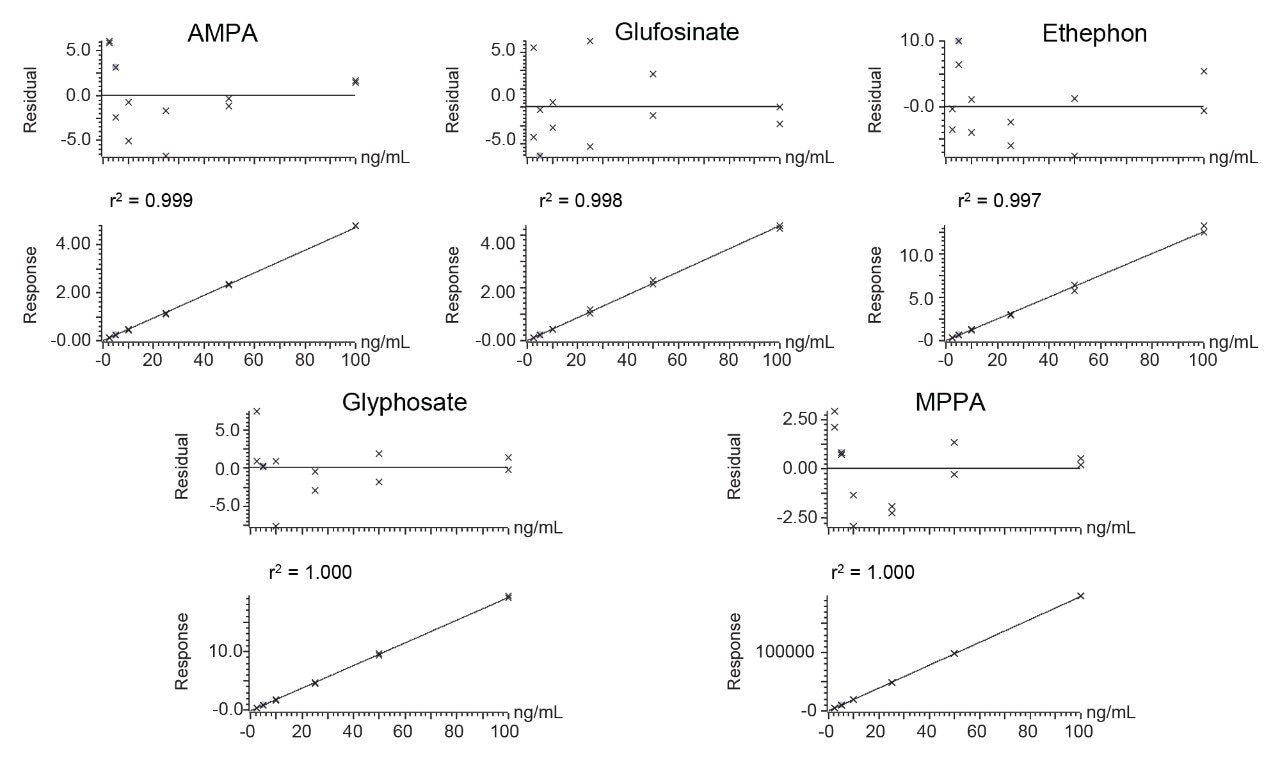
Calibration graphs exhibited excellent linearity of response, using a linear fit with a 1/x weighting (Figure 3); r2>0.99 and residuals <20% except for at higher concentrations in one ethephon and one MPPA graph. These datapoints, at 0.1 and 0.2 mg/kg, were excluded from those calibration graphs as they were not required to calculate the concentration in the spiked extracts.
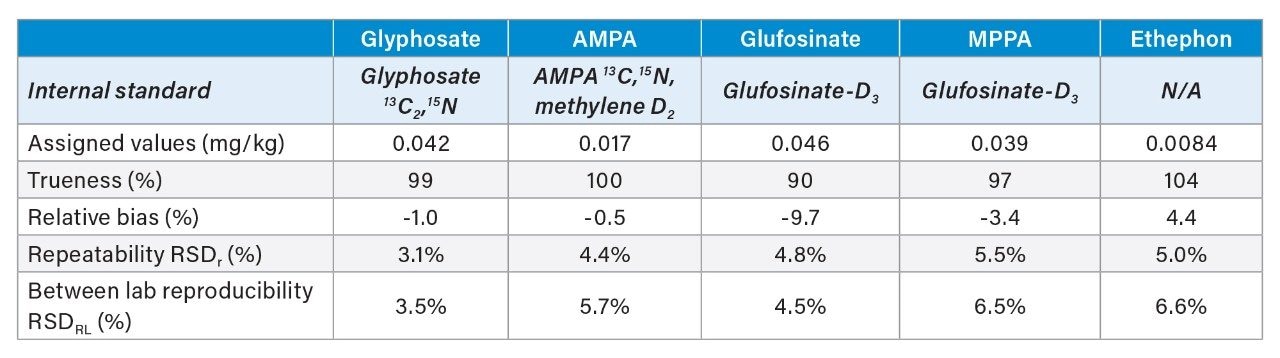
The laboratories demonstrated good accuracy for the quantification of the anionic polar pesticides in the spiked cucumber extract (Table 1). However, one laboratory failed to report results for ethephon. When compared against the assigned values provided by the reference laboratory, trueness was shown to be between 90 and 104% and bias <10%. Values for repeatability within each laboratory (RSDr) and reproducibility between laboratories (RSDRL) were all <7%. Results from the validation are shown in Table 1.
In each case, ion ratios and retention times from the matrix-matched standards agreed well with the criteria specified in the SANTE guidelines, for all compounds except ethephon. Most laboratories struggled with an elevated background on the suggested qualifier transition for ethephon (m/z 143 > 79) and were unable to obtain enough response on this channel to use it for identification purposes for residues 0.05 mg/kg.
The performance of the method for the determination of anionic polar pesticide residues was investigated using an interlaboratory study. Each laboratory successfully implemented the chromatographic method, using the start-up guide, so that the retention times for each compound of interest matched those of the expected reference. Chromatography was shown to be stable and to comply with the SANTE guidelines. The laboratories demonstrated good accuracy for the quantification of the anionic polar pesticides in the spiked cucumber extract. Trueness was shown to be between 90 and 104%, bias no greater than 10% and values for repeatability within each laboratory and reproducibility between laboratories were all <7%.
720007154, February 2021