
This application note describes the use of HPLC-UV which identifies furanocoumarins in grapefruit juice samples. Separations were performed utilizing XBridge Shield RP18 and XBridge C8 Columns.
Scientific observations have revealed evidence that compounds in several common varieties of grapefruit juice impact the oral bioavailability of some prescription drugs. For example, the furanocoumarin bergamottin and the related compound 6,7-dihydroxybergamottin have been shown to inhibit intestinal CYP3A4, a phenomenon termed “the grapefruit juice effect.” Studies have linked this inhibition primarily to fouranocoumains, the majority of which are analogues of bergamottin, 6’-7’-dihydroxybergamottin and 6’-7’-epoxybergamotting, including several dimmers of these compounds.
This report will describe the use of HPLC-UV identify furanocoumarins in grapefruit juice samples. Separations were performed utilizing XBridge Shield RP18 and XBridge C8 Columns.
The juice samples were obtained from white grapefruit. Samples were centrifuged and the furanocoumarins then extracted into ethyl acetate.
|
Columns: |
XBridge Shield RP18, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 μm p/n: 186003009 XBridge C8, 4.6 x 150 mm, 5 μm p/n: 186003017 |
|
Mobile phase A: |
2% Acetic acid |
|
Mobile phase B: |
Acetonitrile |
|
Flow rate: |
0.75 mL/min |
|
Injection: |
20 μL |
|
Temperature: |
Ambient |
|
Detection: |
UV @ 310 nm |
|
System: |
Waters Alliance 2695 with a 996 PDA Detector |
Figure 1 illustrates the reversed-phase HPLC chromatograms of furanocoumarins utilizing both the XBridge Shield RP18 and XBridge C8. The early portions of the chromatograms consist primarily of flavonoids, hydroxycinnamates and their related compounds. The later portions of the chromatorams are dominated by furanocoumarins which demonstrate a distinctive UV spectra with sharp adsorption wavelength maxima near 310 nm and are easily detected using PDA analysis.
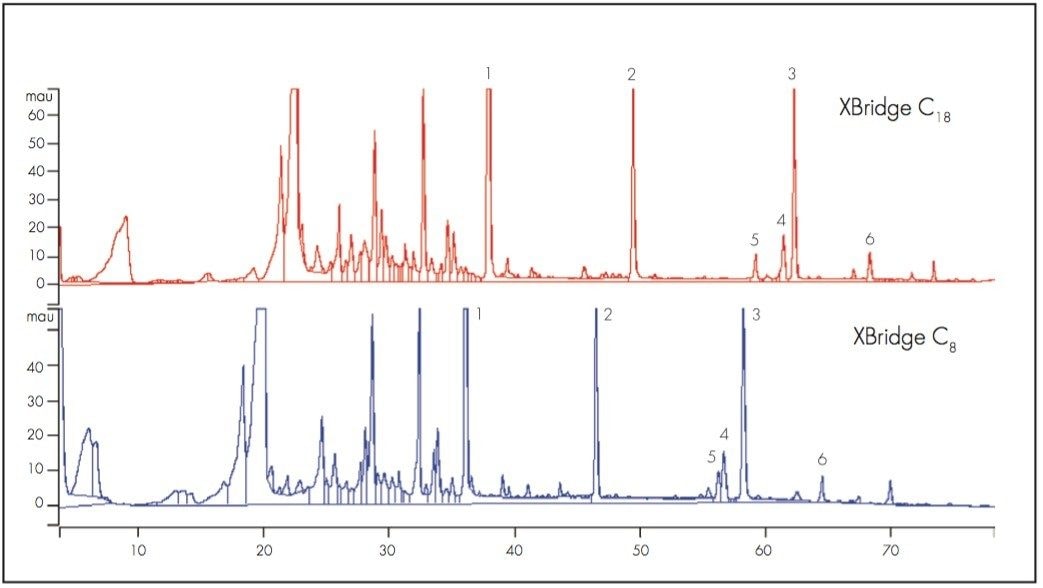
Compounds: (1) 6,7-dihydroxybergomottin; (2) 6’,7’-epoxybergamottin; (3) bergamottin; (4) furanocoumarin dimer; (5) 7-geranyloxycoumarin; (6) furancoumarin dimer.
A limiting factor in the analysis of the function of specific compounds in the grapefruit-drug interaction phenomenon (“the grapefruit juice effect”) is the low level at which many of the active furanocoumarins occur and the ability to accurately identify them. In this study, HPLC analysis utilizing XBridge Shield RP18 and XBridge C8 Columns accurately identified these compounds of interest in a grapefruit juice extract.
Chromatograms courtesy of tUSDA, Agricultural Research Service.
WA60198, April 2008