
This is an Application Brief and does not contain a detailed Experimental section.
This application brief demonstrates to rapidly analyze 23 azo dyes below legislated levels using Waters ACQUITY UPLC H-Class System, coupled with the ACQUITY QDa Detector.
Provides a rapid, easy, and selective quantification method for prohibited azo dyes at 100 times below the legislative limits.
Azo dyes are a class of synthetic organic dyes which are widely used in the coloring process of consumer goods such as textiles, leather, and cosmetic products. However, some of these dyes can degrade under certain conditions and be reduced to aromatic amines. Twenty-two aromatic amines are currently classified as carcinogens or potential carcinogens under European Union (EU) regulation (EC 1907/2006).
Under the EU regulation and REACH 1907/2006/Annex XVII, the threshold limit for each of these prohibited amines in a product is 30 ppm. Current official test methods EN 14362-1:2012 describe the methods for determining certain aromatic amines derived from azo colorants. Whereas EN 14362-3:2012 describes the methods for determining certain aromatic amines which may release 4-aminoazobenzene.
The analysis time described in the current test method (EN 14362-1:2012) for HPLC (UV or MS/MS) and GC-MS are 35 mins and 18 mins respectively.
To address the increasing demands of higher sample throughput while meeting legislative requirements, Waters has developed a solution for the textile and leather industries that employs the ACQUITY UPLC H-Class System with the ACQUITY QDa Detector.
The ACQUITY UPLC H-Class System with the ACQUITY QDa Detector was used to monitor a total of 23 azo dyes including 20 azo dyes that are prohibited under the EC 1907/2006 legislation. Minimal method development is needed as the pre-optimized source parameters in the ACQUITY QDa Detector provide the required sensitivity for azo dyes analysis. Harnessing the performance of UPLC increased peak resolution and enhanced sensitivity with a run time of 5.5 minutes has been developed for each analysis.
Azo dyes were monitored according to their respective retention time and Single Ion Recording (SIR) mass-to-charge ratio (m/z), as described in Table 1. Single Ion Recording provides better sensitivity and selectivity as compared to HPLC-UV analysis. The SIR chromatograms shown in Figure 1 indicate that these dyes can easily and selectively be detected at 100 times below the legislative limits.

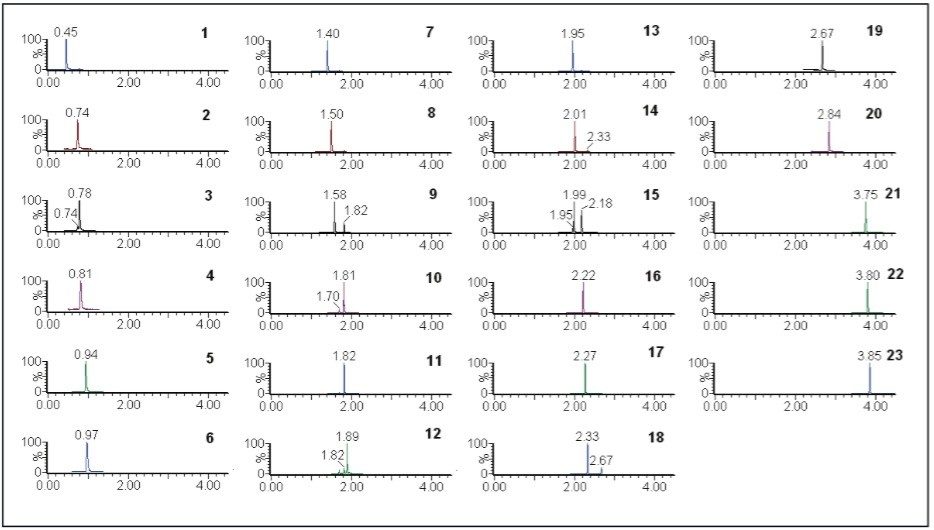
Quantification of these azo dyes was also carried out with concentrations ranging from 0.3 to 2 ppm, and linearity of >0.996 was achieved for all 23 azo dyes. Replicates injections (n=5) of 300 μg/kg of azo dyes compounds showed excellent reproducibility with an average RSD of <3.1%. The calibration curve and replicate injections of 4-aminoazobenzene are shown in Figure 2.
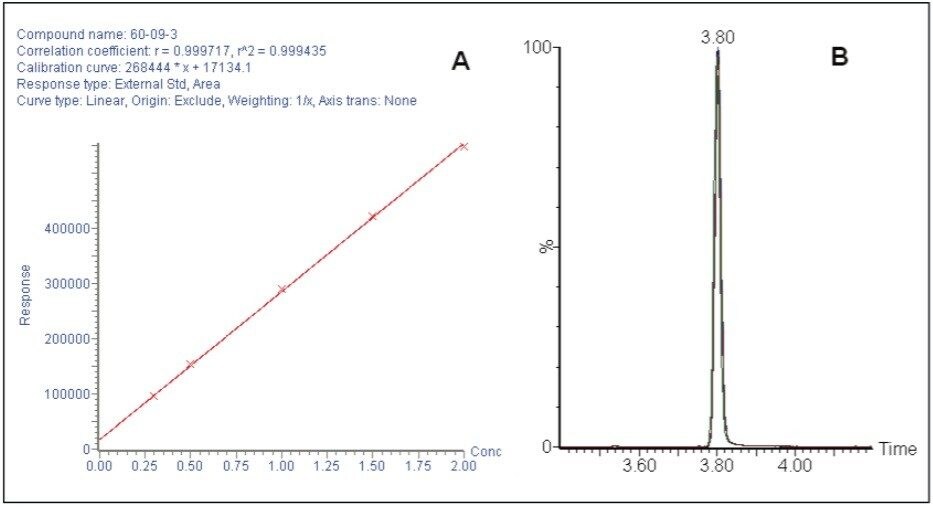
Waters ACQUITY H-Class System with the ACQUITY QDa Detector provides increased confidence in the identification and quantification of azo dyes as compared to HPLC/UV. Besides sensitivity and selectivity, the ACQUITY QDa Detector can be effortlessly integrated into current LC analysis methods with minimal method development. By leveraging UPLC technology, reduced analysis times and a reduction in solvent usage can also be achieved.
720005096, July 2014