This application note describes a simple LC-MS method for the analysis of a Vitamin B12 standard.
With the use of the Waters Atlantis C18 Column, Vitamin B12 was well retained, with a good peak shape
Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamine) is a water-soluble vitamin that has important physiological function in the human body. Vitamin B12 has the ability to make folic acid available to bone marrow, which appears to be necessary for red blood cell formation. A Vitamin B12 deficiency leads to a degeneration of both the sensory and motor columns in the spinal cord with loss of sensation and paralysis. As a result, people need approximately 1–2 μg of Vitamin B12 per day.
The determination of Vitamin B12 is important, but can be challenging largely because of its chemical instability and the complexity of the matrices in which it is usually found. Ideally, methods for Vitamin B12 analysis should be simple, selective and sensitive to overcome the above issues. The most commonly reported method for Vitamin B12 analysis is reversed-phase HPLC separation with various detection schemes such as UV, fluorescence, chemiluminescence, etc. However, most of these methods are tedious and time consuming. Phosphate buffers are usually called for in order to obtain sufficient LC separation.
In this application note, we describe a simple LC-MS method for the analysis of a Vitamin B12 standard. A Waters Atlantis C18 Column, with superior retention for polar compounds and the ability to operate in 100% aqueous conditions, was used for the separation. A Waters Micromass ZQ 4000 single quadrupole mass spectrometer was used for detection. With the selectivity and sensitivity offered by the MS detector, the method simply used a binary acetonitrile/water gradient without the need for a buffer or ion pairing reagents.
|
LC system: |
Alliance HT Separations Module |
|
Column: |
Atlantis C18 2.1 x 150 mm, 3.5 μm |
|
Flow rate: |
0.2 mL/min |
|
Mobile phase: |
Acetonitrile (A) Water (B) |
|
Injection volume: |
10 μL |
|
Time(min) |
%A |
%B |
Curve |
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
0 |
100 |
1 |
|
1 |
0 |
100 |
1 |
|
8 |
40 |
60 |
6 |
|
10 |
60 |
40 |
6 |
|
11 |
0 |
100 |
11 |
|
Mass spectrometer: |
Micromass ZQ 4000 Mass Spectrometer |
|
Ion mode: |
ESI+ |
|
Capillary voltage: |
3.5 kV |
|
Cone voltage: |
80 V |
|
Source temp.: |
105 °C |
|
Desolvation temp.: |
180 °C |
|
Desolvation gas flow: |
365 L/Hour |
|
Cone gas flow: |
50 L/Hour |
|
Inter channel delay: |
0.02 s |
|
Inter scan delay: |
0.02 s |
|
Dwell time: |
0.08 s |
Full scan spectra of Vitamin B12 were obtained during the optimization of the MS parameters, as shown in Figure 1. Acquisition parameters were optimized in order to select the proper ion for selected ion monitoring (SIR) experiments and to determine an optimum cone voltage. The protonated molecule [M+H]+ at m/z 1356 was obtained at a cone voltage of 50 V with good intensity (4.41e5). However, the Vitamin B12 showed fragmentation into many other ions, which reduced the intensity of the [M+H]+ ion. The spectrum at 80 V was cleaner with higher ion intensity (6.14e5) at m/z 913. As a result, the ion at m/z 913 was chosen to be the ion to monitor for the SIR experiments and cone voltage of 80 V was chosen as the optimum for the ion at m/z 913.
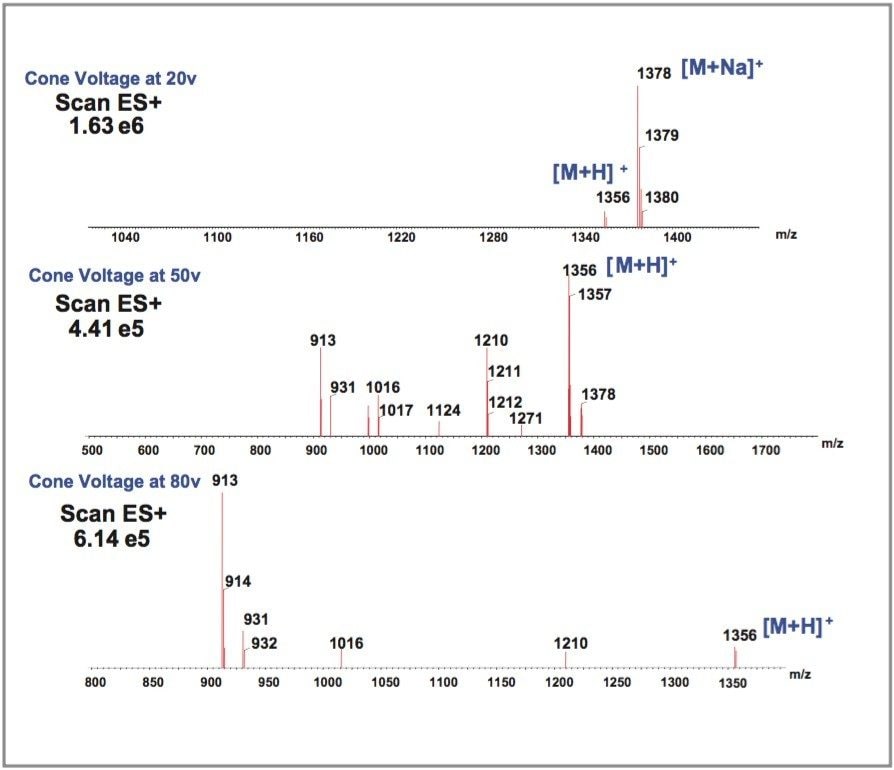
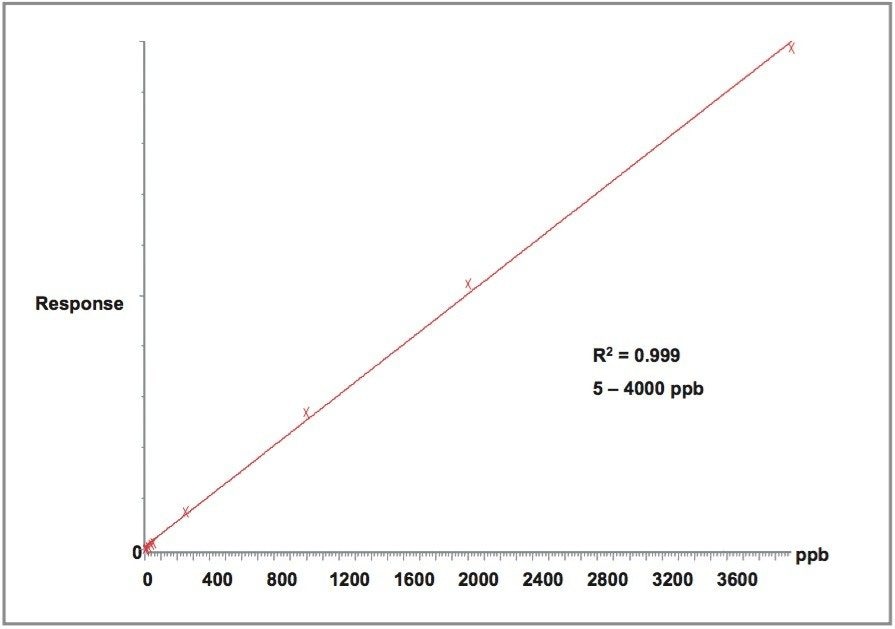
Figure 2 shows the calibration curve of Vitamin B12. The linear range was from 5 to 4000 ppb. With the Waters Atlantis C18 Column, this water-soluble vitamin was well retained with an excellent peak shape. Figure 3 shows the SIR chromatograms of Vitamin B12 at m/z 913 at different concentrations. The signal-to-noise ratio at 2 ppb was 5, and at 5 ppb was 50.
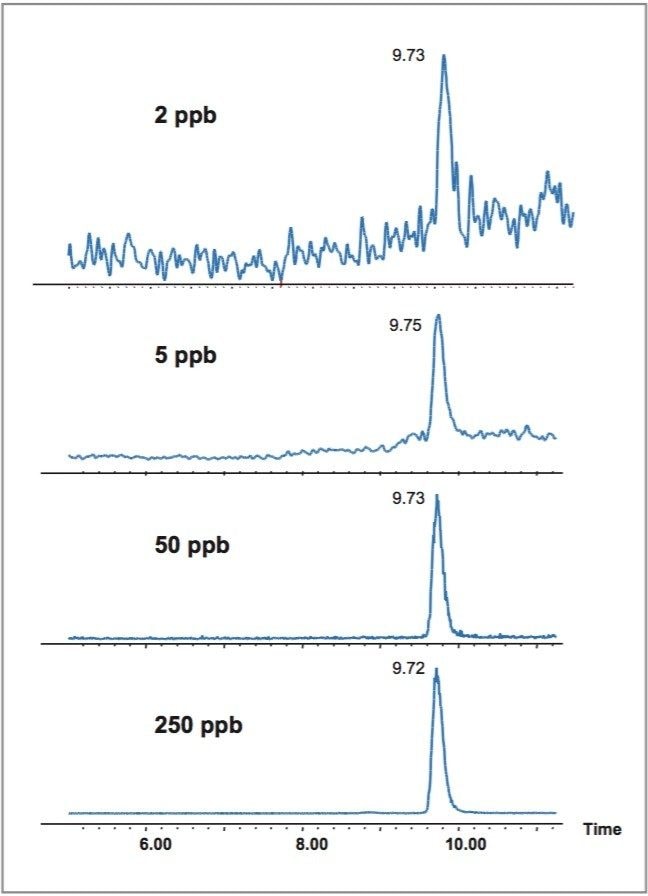
A simple LC-MS quantification method for Vitamin B12 was described. With the use of the Waters Atlantis C18 Column, Vitamin B12 was well retained, with a good peak shape. A simple binary gradient was used without adding buffer. The quantification linear range was from 5n to 4000 ppb. The limit of detection with a 10 μL injection was 2 ppb.
720000758, September 2003