
This work demonstrates the applicability of a simplified SPE method using Oasis PRiME HLB μElution Plates for the analysis of COOH-THC in authentic urine samples.
The data obtained demonstrates that the use of Oasis PRiME HLB enables a clean extraction without the need for conditioning or equilibration and gives quantitative results equivalent to a fully validated method.
Cannabis continues to be the most widely abused recreational drug in the United States. In addition, the growing number of states legalizing cannabis for medical and/or recreational purposes means that there is a growing need for analytical methods for the quantification of THC and its metabolites. We have recently developed a simple, rapid, and clean SPE extraction method for these analytes using Oasis PRiME HLB.1 While this method demonstrated excellent accuracy over a wide calibration range, a side by side comparison with a fully validated method from an external laboratory is a key component of method validation. This application note details an inter laboratory comparison of COOH-THC quantification using Oasis PRiME HLB.
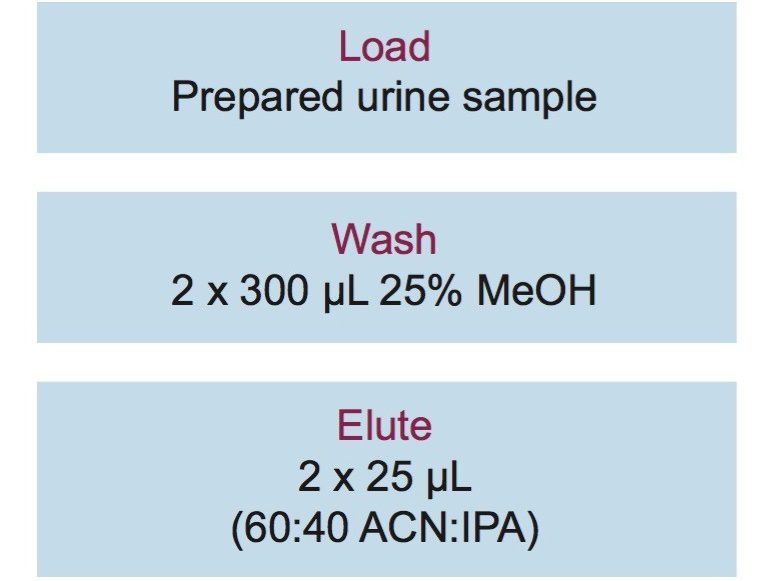
Authentic urine samples were obtained from an outside lab that conducts toxicology tests. Samples were prepared as follows: 25 µL of internal standard (100 ng/mL) was added to 350 µL of urine. 320 µL of 50% KOH was added and the samples were incubated for 2 hours at 65 °C to hydrolyze the COOH-THC glucuronide. 75 µL of the pretreated sample was added directly to the wells of an Oasis PRiME HLB µElution Plate (p/n 186008052). All samples were washed with 2 x 300 µL of 25:75 MeOH:H2O and eluted with 2 x 25 µL of 60:40 ACN:IPA. The samples were then diluted with 100 µL of 40% ACN in water. 5 µL was injected onto the UPLC-MS/MS system. The SPE procedure is shown in Figure 1.
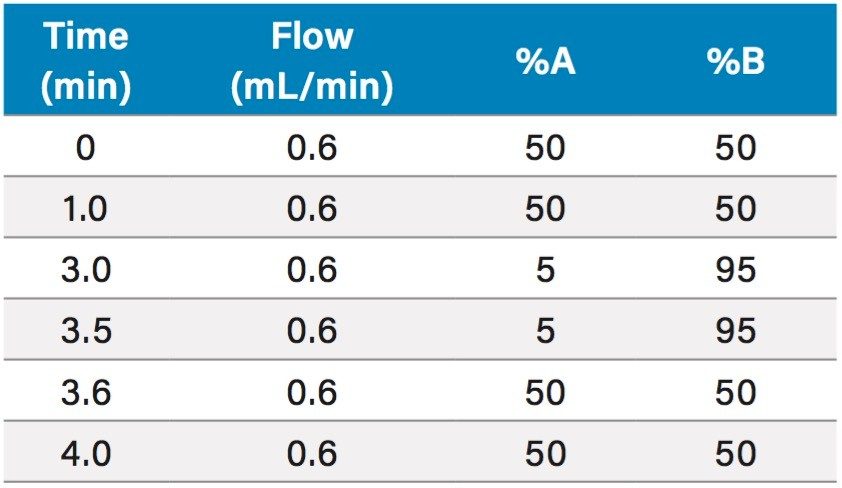
Mobile phases A and B consisted of 0.1% formic acid in water (MPA) and ACN (MPB). The LC gradient is shown in Table 1. Separation was achieved on an ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18, 1.7 µm, 2.1 x 50 mm Column (p/n 186002350) at a temperature of 40 °C.
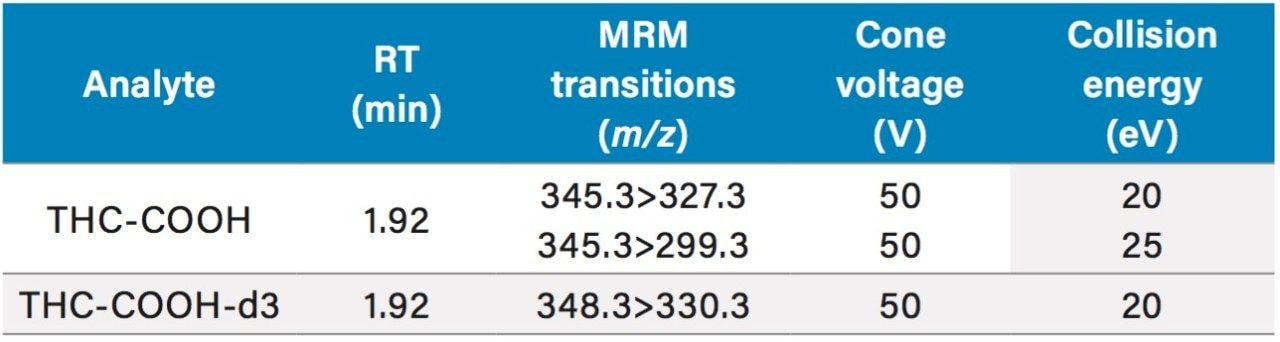
Detection was achieved with a Xevo TQ-S. MRM parameters are listed in Table 2.
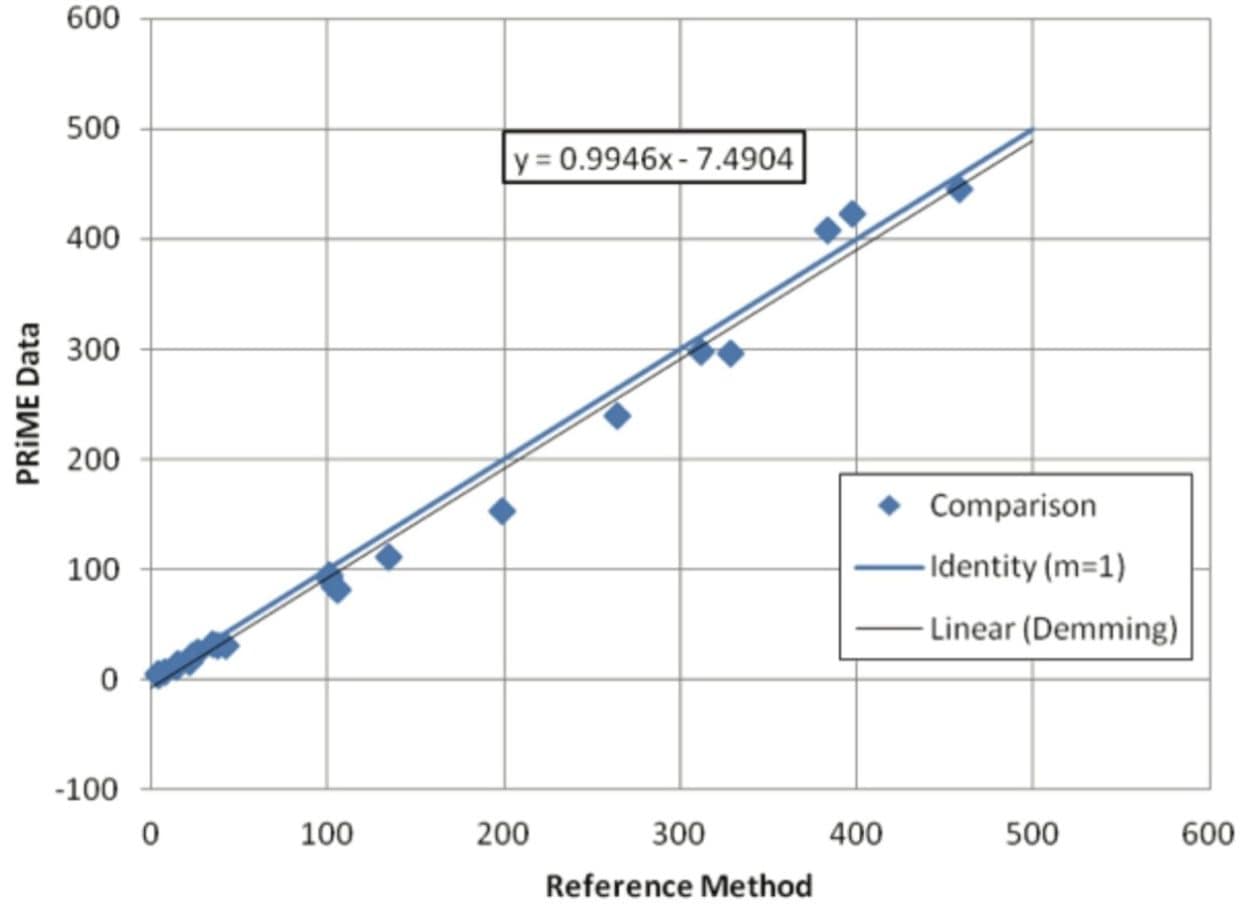
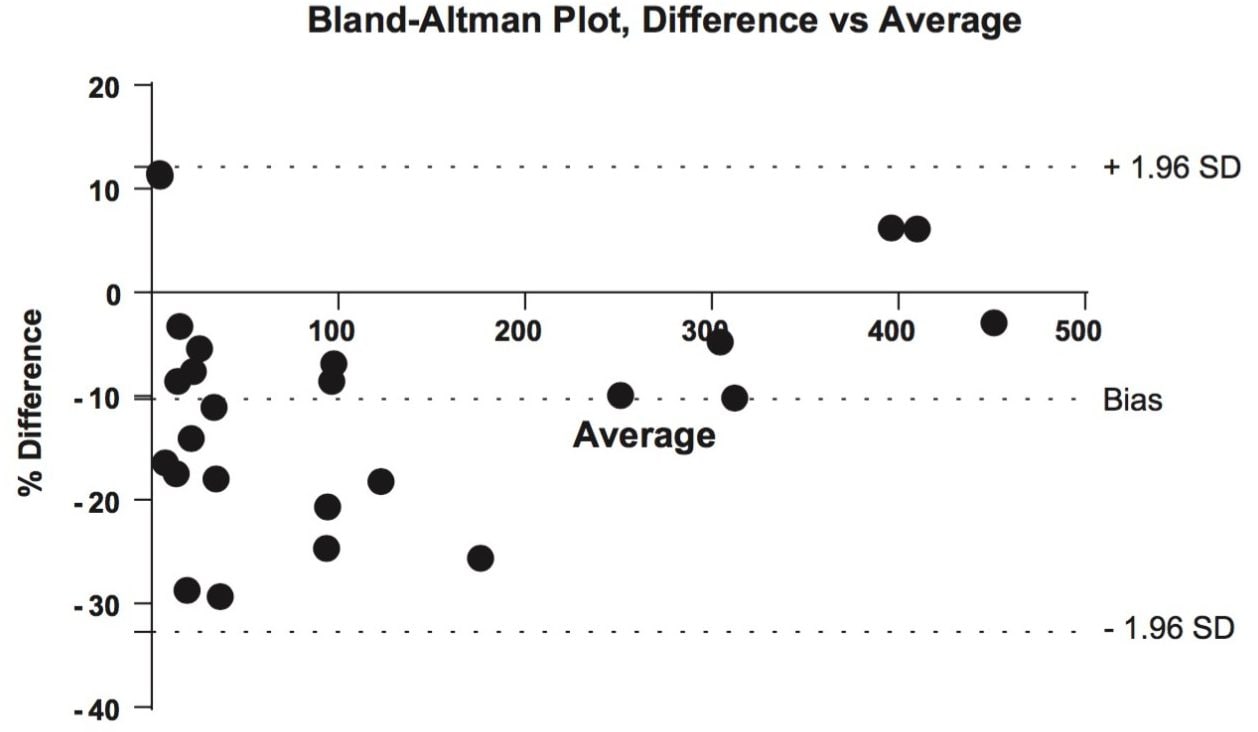
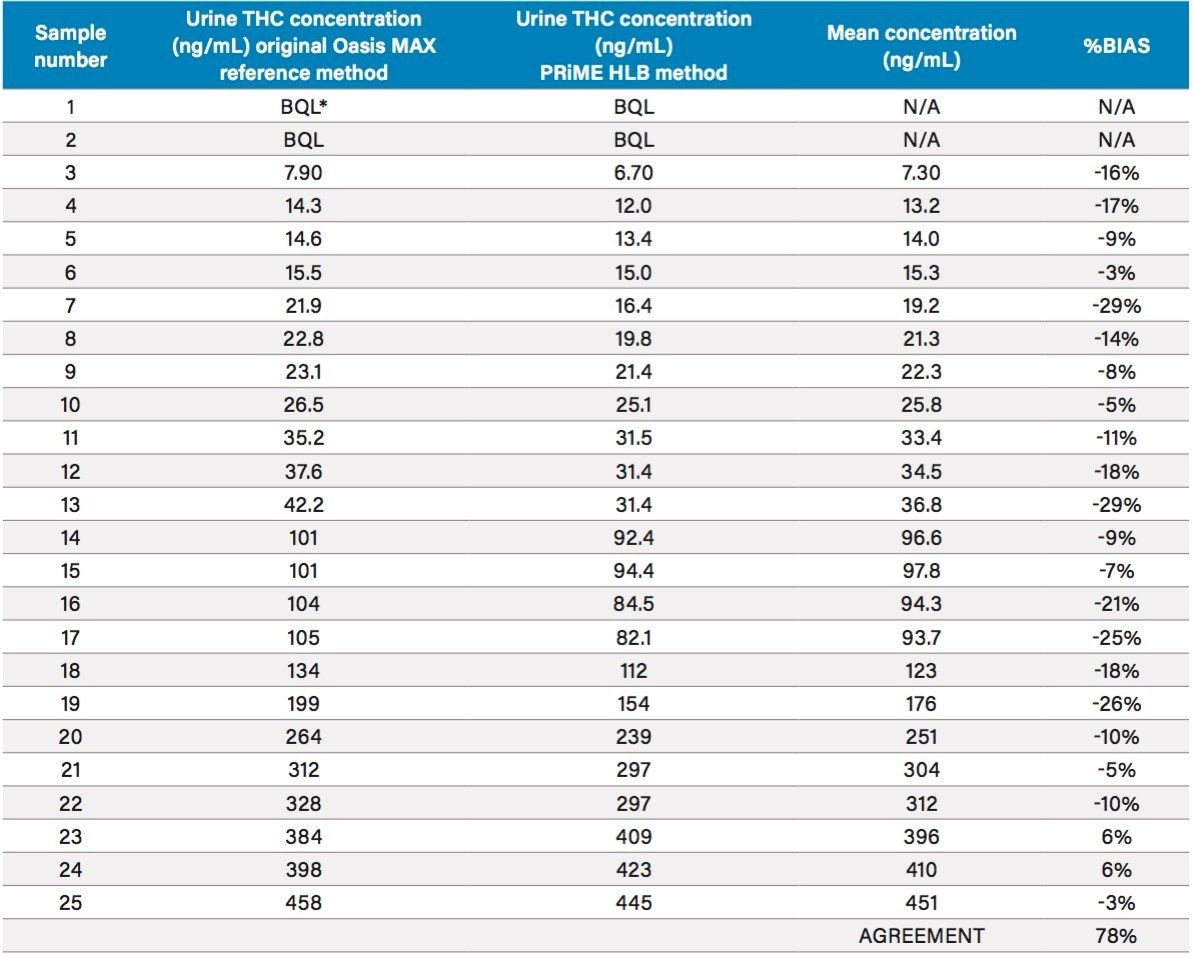
25 authentic urine samples were analyzed and compared to the validated comparison method. The samples ranged in concentration from 6.70–458 ng/mL, covering nearly the entire linear range of the reference method (5.00–500 ng/mL). A Deming regression (Figure 2) had a slope of 0.995 demonstrating parallelism between the two methods. The correlation (R) of 0.998 indicated an excellent correlation between the results obtained by the two laboratories. The Bland-Altman plot for the Oasis PRiME HLB method for the analysis of COOH-THC in authentic urine samples vs. reference method indicated that the two sets of data are similar at 95% limits of agreement (Figure 3). Table 3 details the results obtained by the two methods. 78% of the sample results are within 20% of each other, exceeding the FDA-GLP specification of 67% for incurred sample reanalysis.2 Most results showed a slight negative bias not seen in the standards or QCs. Since the standards and QC samples were prepared in surrogate matrix (Surine), it is possible that the combination of different SPE methods and different chromatographic conditions differentially remove or chromatographically resolve an endogenous substance from the urine samples causing slight signal suppression during ionization. Despite the fact that the samples were subject to different extraction procedures as well as different LC-MS/MS conditions, the results show excellent agreement and indicate that the simplified SPE methodology, which eliminates conditioning and equilibration, gives equivalent results for authentic urine samples.
This work demonstrates the applicability of a simplified SPE method using Oasis PRiME HLB µElution Plates for the analysis of COOH-THC in authentic urine samples. Correlation was excellent with a validated method from Dominion Diagnostics that used a different SPE protocol and LC-MS/MS analysis procedure. Previous work had shown that Oasis PRiME HLB had excellent recovery with very low variability and could nearly eliminate matrix effects in urine samples. These data demonstrate that the differences between different samples do not affect the quantification of COOH–THC. The use of Oasis PRiME HLB enables a clean extraction without the need for conditioning or equilibration and gives quantitative results equivalent to a fully validated method.
720005869, December 2016