
This is an Application Brief and does not contain a detailed Experimental section.
This application brief demonstrates a simple method to provide an analytical solution for a selection of cationic surfactants using reversed-phase solvents and the mixed-mode Waters Atlantis PREMIER BEH C18 AX Column.
The analysis of quaternary ammonium compounds has long presented a challenge analytically, due to the poor peak shapes obtained for these compounds under reversed-phase conditions. The development of the mixed-mode Atlantis PREMIER BEH C18 AX Column allows us to demonstrate excellent peak shapes for three cationic surfactants.
Surfactants are used extensively in the cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and agricultural industries covering a diverse range of uses, from antimicrobial agents to anti-static agents. Due to their amphiphilic nature (i.e., possessing both a polar hydrophilic and non-polar hydrophobic region), they represent a challenge analytically.
Cationic surface-active agents often contain nitrogen atoms carrying a positive charge (mainly in an amine or quaternary ammonium group), which are coupled with one or several long alkyl chains. Quaternary ammonium compounds (QACs) are one of the widest applied groups of cationic surfactants.¹
HPLC is commonly employed for surfactant analysis, however using a conventional reversed-phase (RP) separation can struggle to retain these compounds due to retention and peak shape issues. Ion-pair chromatography (IPC) and gas chromatography (GC) are also used but suffer from long equilibration and run times, with GC often relying on analyte derivatization, which is time consuming and has the potential to introduce sample preparation errors and/or variation.
The challenge of those strategies has led to the development of mixed-mode RP/ion-exchange (IEX) columns, which contain stationary phases having both hydrophobic and IEX functionalities.2
However, many mixed-mode RP/IEX columns suffer from poor batch-tobatch reproducibility and poor hydrolytic stability. To overcome these issues, Waters has developed a new RP/anion-exchange (AX) stationary phase based on hybrid organic/ inorganic particles that has excellent batch-to-batch reproducibility and is stable over a wide pH range. This material is packed into new MaxPeak High Performance Surfaces (HPS) column hardware, which is designed to increase analyte recovery by minimizing interactions with stainless steel that can lead to analyte loss.3
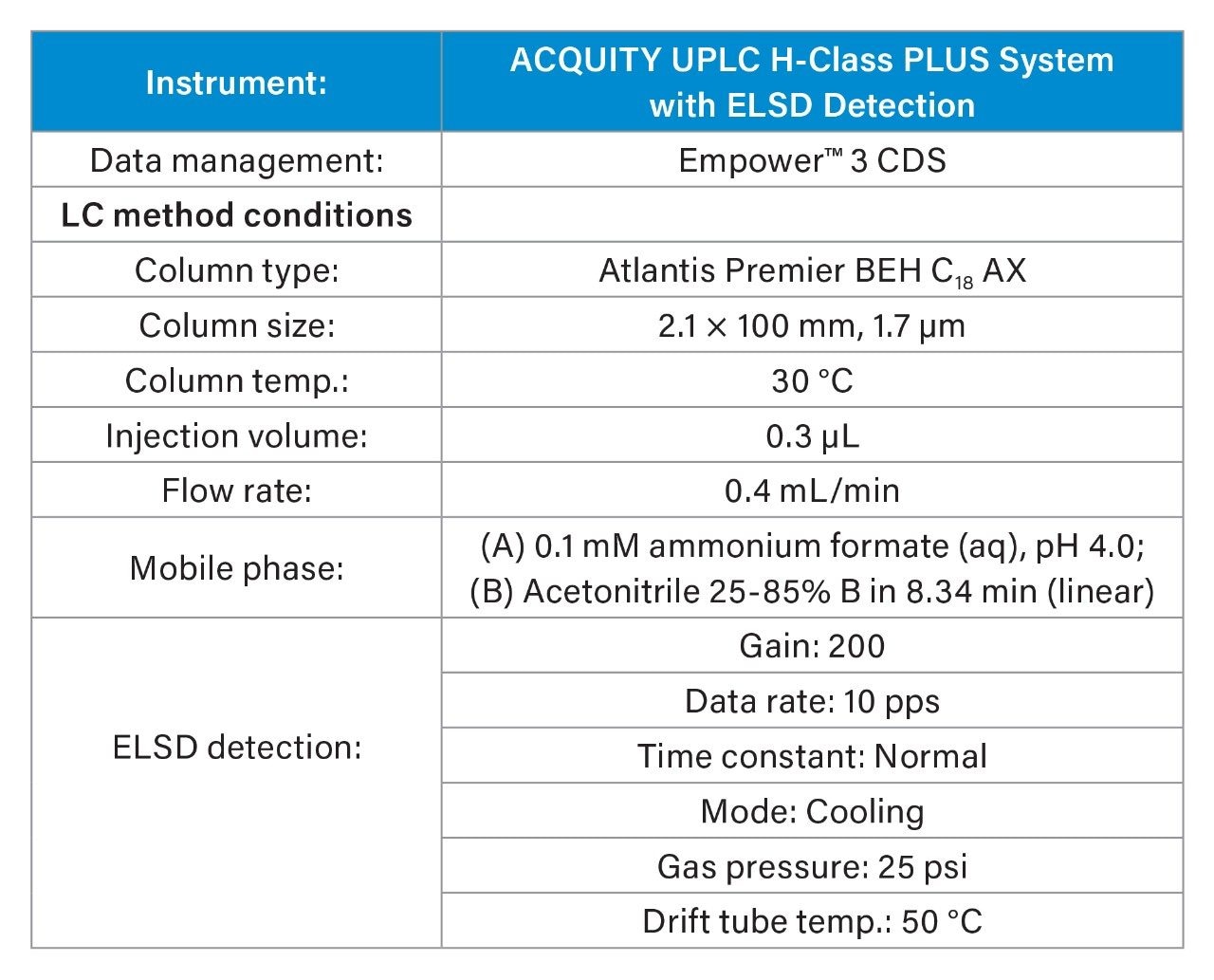
In this application brief, we demonstrate the separation of a mixture of three cationic surfactants (detailed in Figure 1) with the goal of achieving good retention, baseline separation, and good peak shape.
The samples were run on an ACQUITY UPLC H-Class PLUS System equipped with an evaporative light scattering detector (ELSD), as some of the compounds tested exhibit weak/no chromophore.
Analytical standards of all compounds detailed in Figure 1 were sourced from Sigma-Aldrich (Poole, UK). A solution containing all three compounds was prepared in water and injected directly. The samples were analyzed using the method conditions detailed in Table 1.
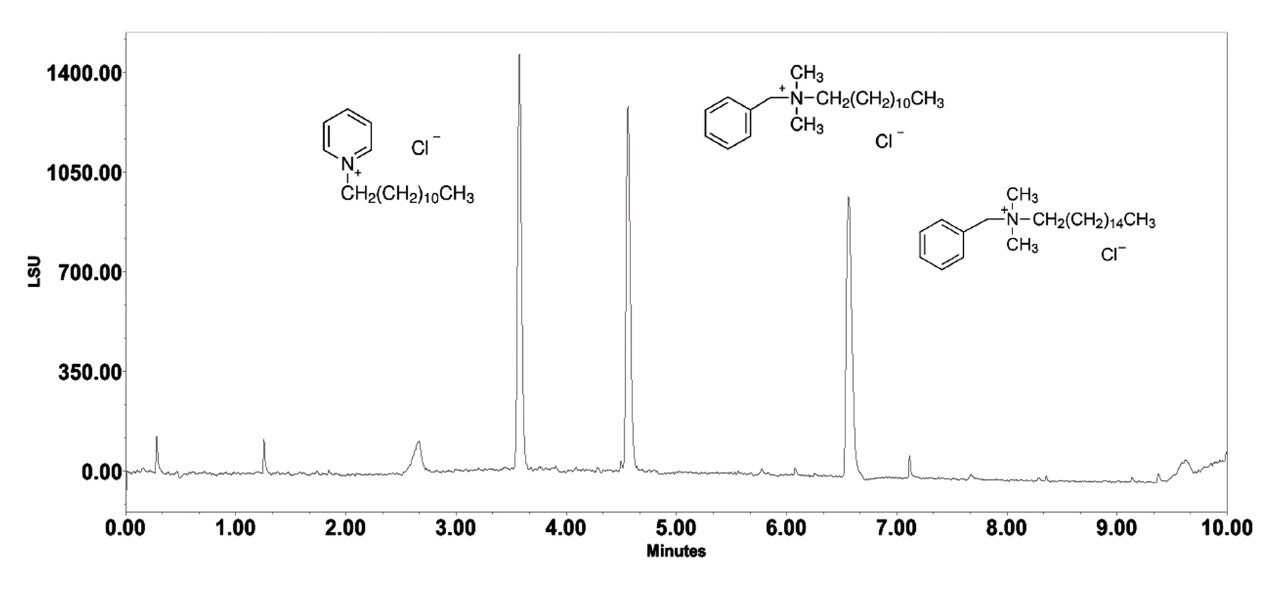
The Atlantis PREMIER BEH C18 AX Column successfully separated the QACs with full baseline resolution, while exhibiting excellent peak shape in a 10-minute runtime (Figure 2).
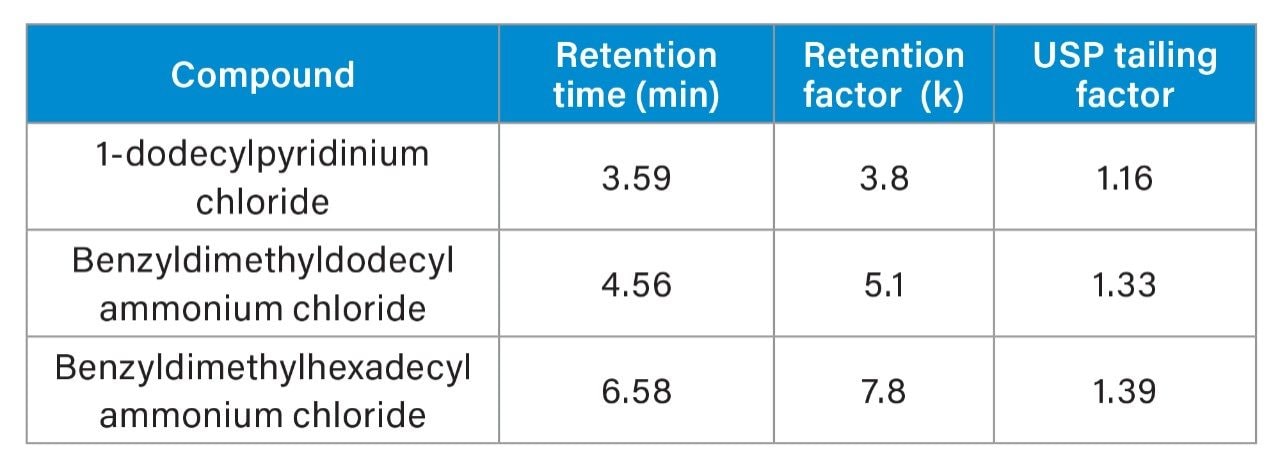
Good retention was observed for all three compounds with retention factors (k) of 3.8, 5.1, and 7.8, and tailing factors of 1.16, 1.33, and 1.39 for 1-dodecylpyridinium chloride, benzyldimethyldodecyl ammonium chloride, and benzyldimethylhexadecyl ammonium chloride, respectively (Table 2).
The mixed-mode Atlantis PREMIER BEH C18 AX Column has proven its effectiveness for the analysis of a mixture of three QACs using reversed-phase solvents without the need for derivatization or ion-pairing reagents.
This simple method demonstrates how this column can provide a straightforward analytical solution for a traditionally challenging group of compounds.
720006746, March 2020